Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
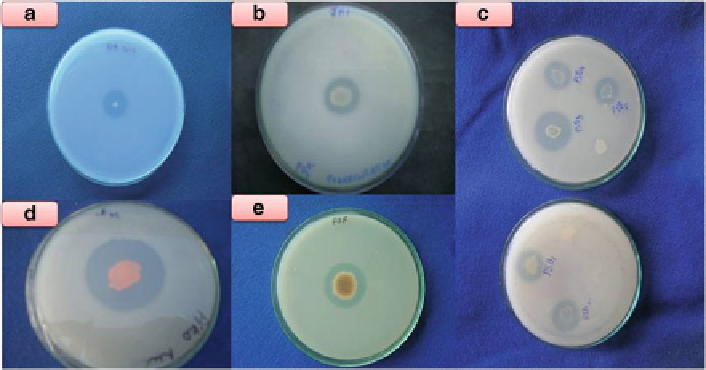
Plate 1.1
Phosphate solubilization on Pikovskaya plate by some notable P solubilizers. (
a
)
Bacillus
,(
b
)
Azotobacter
,(
c
)
Serratia
,(
d
) Fungi, (
e
)
Pseudomonas
sp.
under liquid culture medium. Finally, the efficient P-solubilizing organisms are
selected and used for the development of inoculants whose performance is tested
under pot/field environments against various crops of economic importance.
1.5.3 Bioassay of P-Solubilizing Activity
The microbial strains expressing PS activity during screening process are further
enriched by inoculating into the Pikovskaya medium, incubated at 28
2
C for
7 days and then observed on solid plates for halo formation. The solubilization
index (SI) and solubilizing efficiency (SE) of such microbes are calculated by the
formula suggested by Premono et al. (
1996
)as
ðÞ¼
colony diameter
zone of halo
=
Solubilization Index SI
þ
colony diameter
ðÞ¼
zone of halo
colony diameter
Solubilizing Efficiency SE
100
=
The colonies forming clear halo around microbial growth indicating P solubili-
zation are counted and further used to determine the relative P-solubilizing effi-
ciency [RPSE] in liquid Pikovskaya medium. The clear halo around bacterial
growth is measured, and cultures are further used to determine the extent of P
solubilization in liquid Pikovskaya medium. For quantitative measurement, 100 ml
of Pikovskaya broth containing 5 g TCP is inoculated with 1 ml of 10
8
cells/ml of
each culture. The flasks are incubated for 5, 10 and 15 days with shaking at 120 rpm
at 28
2
C. A 20 ml culture broth from each flask is removed and centrifuged
(9,000
g
) for 30 min, and the amount of water-soluble P released into the