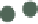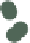Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
scatter propval100 ownhome,
xsize(3) ysize(1)
Here, we make a graph to illustrate how
to use
xsize()
and
ysize()
to control
the aspect ratio of the graph, as well as
the size. Note that when we do this,
the size of the graph will not change on
the screen but the aspect ratio will.
Although we can size the graph on the
screen, when we export the graph, it
will have both the size and aspect ratio
we chose using
xsize()
and
ysize()
.
Uses allstates.dta & scheme vg s1c
40
50
60
70
80
% who own home
scatter propval100 ownhome,
xsize(2) ysize(2)
Here, we make just one more graph to illustrate that we
can use
xsize()
and
ysize()
to control the aspect
ratio of the graph, as well as the size. Here, we make
the graph square by making the graph 2 inches high by
2 inches tall.
Uses allstates.dta & scheme vg s1c
40
50
60
70
80
% who own home
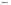
scatter propval100 ownhome,
scale(1.7)
In this example, we add the
scale(1.7)
option to magnify the sizes
of the text and markers in the graph,
making them 1.7 times their normal
sizes. This can be useful when we make
small graphs and want to increase the
sizes of the text and markers to make
them easier to see.
Uses allstates.dta & scheme vg s1c
40
50
60
70
80
% who own home
The electronic form of this topic is solely for direct use at UCLA and only by faculty, students, and staff of UCLA.