Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
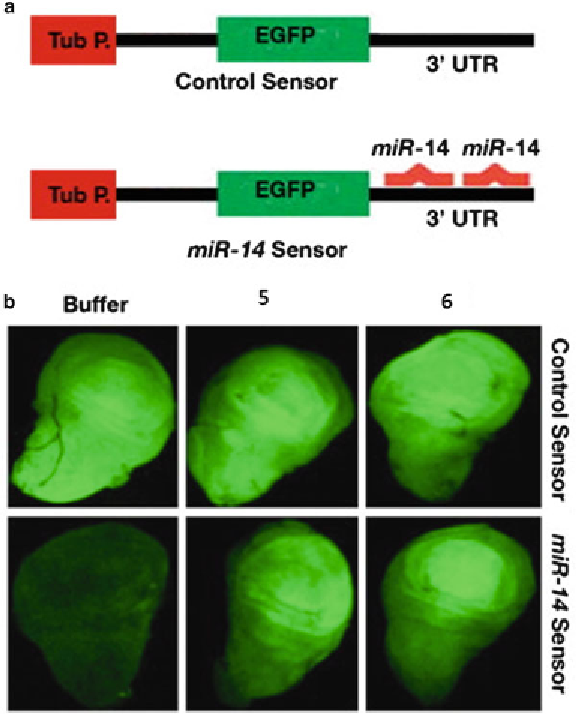
Fig. 4
Aza-fl avone inhibition of miR-14 in larval wing discs. (
a
) Schematic of the
reporter constructs with either a control sequence with no sequence homology
to a miRNA in the 3
′
UTR of EGFP or a functional reporter with two miR-14-
binding sites in the 3
UTR. (
b
) EGFP expression in larval discs harboring either
the control sensor or the miR-14 sensor in the presence and absence of com-
pounds
5
and
6
. EGFP expression is signifi cantly higher in the miR-14 construct
treated with one of the small-molecule inhibitors. Image adapted with permis-
sion from Chandrasekhar S et al. (2012) Bioorg Med Chem Lett
′
true effi cacy of these compounds in more relevant in vivo disease
models; however, this research effectively demonstrates that lower-
ing the cellular concentrations of pri-miRNAs with small molecules
can affect mature miRNA levels and exert a biological consequence,
specifi cally towards cancer cell viability.
2.2 Inhibition of
Drosha-Mediated
Pri-miRNA Maturation
In Vitro
The inhibition of pri-miRNA maturation is also feasible via the
disruption of Drosha processing in the nucleus, inhibiting the for-
mation of pre-miRNA. While no small-molecule inhibitor of this
processing has been discovered, different oligonucleotide