Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
„traditional“ control applications
„traditional“ management applications
Applications
„traditional“ management paths
„traditional“
protocol
stack
TCP/IP
network
interface
management
node interacts
in a traditional way with other
DC nodes and also with self-
organizing f unctions
controller activates
and interacts with
self -organizing control /
management f unctions
management
domain
OFC
control domain
NW domain
VMs
VMM
switching
switching
network
interface
network
interface
IT domain
network switch (OFS)
physical server
implant leightweight, task-specific and self -
organizing control / management f unctions
OpenFlow switching on physical servers
would for NW/IT joint self -organization
task specific and self -organizing control /
management f unctions on application layer
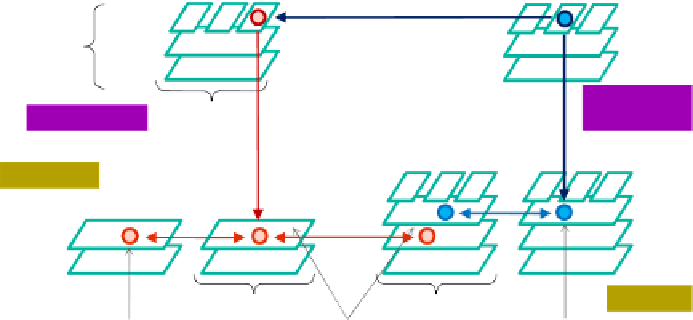
Fig. 4.
Application of management capabilities to a converged IT/network system.
In this figure, SNMP in a weakly distributed form, OpenFlow centralized
control, and INM distributed network management with objectives on the IT
side are all combined in a single architecture. The figure shows in particular
how centralized approaches merge with decentralized management functions,
that is, INM. To provide uniform handling of the technologies, adapters are
used that encapsulate e.g. SNMP agents to allow standardized communication
between management capabilities of other types of management and control
protocols. Note in particular the resulting homogeneous switching layer,
where each network element (including servers) supports OpenFlow
switching functionality homogeneously.
4.2 Scenario Description
The scenario we consider is a data center with IT and network resources,
and virtualization. We consider two use cases that are closely linked: 1)
anomaly (congestion) detection, and 2) virtual machine migration with flow
rerouting that follows after an anomaly has been detected (also see
Fig. 5
).
Assumptions
1)
An anomaly occurs locally, e.g. due to the exhaustion of CPU capacity
at a host because of high load that is incurred by virtual machines.
2)
Local performance checks find out about other physical hosts to which
some virtual machines may be migrated.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search