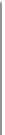Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Vertical
Sun
q
h
Horizontal
Noon
90
21 June
80
22 December
70
60
Sunrise
Sunset
50
40
30
20
10
0
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
Solar time
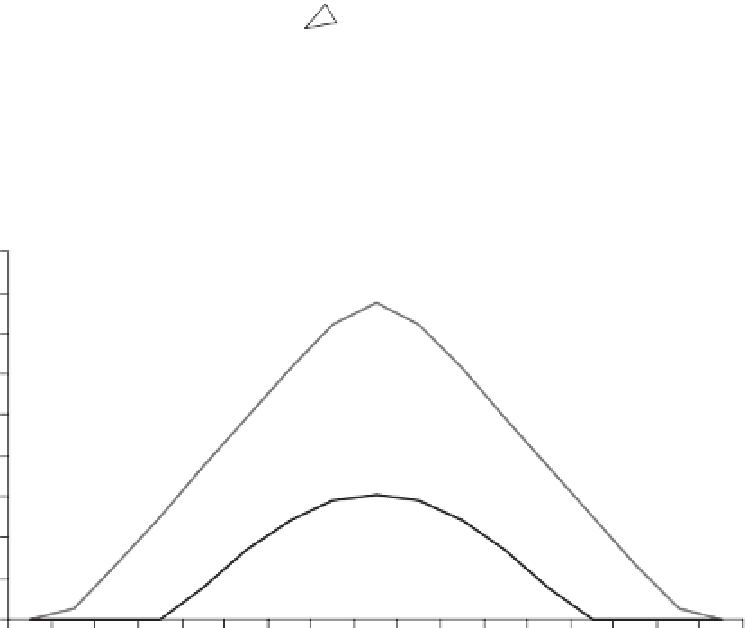
Fig. 2.8.
evolution of solar elevation (
h
) through the day in the summer and winter solstices for the south
of Spain (latitude 37°N).
q
is the zenith angle.
On completely cloudy (covered) days,
the percentage of total direct solar radiation
in relation to the global radiation is almost
negligible.
Like all electromagnetic radiations, solar
radiation propagates in the form of waves.
The quality of solar radiation is character-
ized by its wavelength, measured in nano-
metres (nm). It can also be defined by its
frequency (related to the wavelength). Plate 1
shows a sketch of the different radiations, by
wavelength (or spectral composition).
The light is the radiation that stimu-
lates the vision sensation in the normal
human eye (photo-optical response). This
response covers the wavelengths ranging
from 380 to 720 nm, with a peak response
around 550 nm. The colour, as a chromatic
response of the human eye, ranges from 400
to 500 nm for the blue, 500-600 nm for the
green, 600-700 for the red and 700-800 for
the far red (Langhams and Tibbitts, 1997).
In the limit of the Earth's atmosphere,
solar radiation ranges from 200 to near