Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
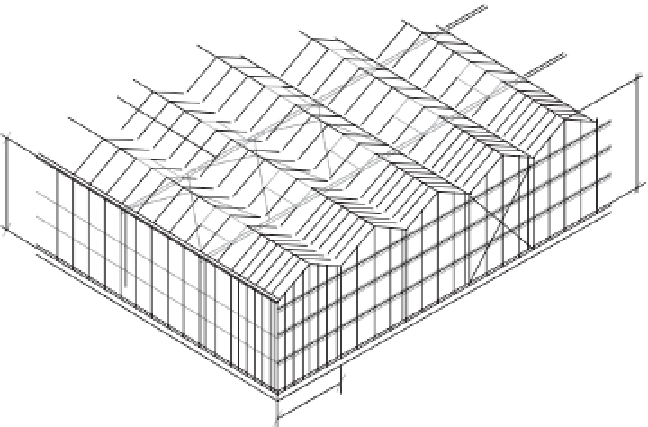
4.8-5.5 m
4.0-4.5 m
3.2-4.0 m
Fig. 4.16.
Glasshouse structure, Venlo type.
4.8
Greenhouse Site Selection
•
Protection from cold winds (usually
from the north in the northern hemi-
sphere), using windbreaks or taking
advantage of the topography. If snow is
to be expected, the greenhouse must be
far away from trees to avoid snow
accumulation.
Supply of irrigation water, in sufficient
The specific selection of the location of the
greenhouse must take into account aspects
such as:
•
Topography. In principle, the place
must be flat in the width direction, with
a slope along the main axis between 0
and 0.5% (never more than 1-2%,
which would involve it being terraced).
In some cases, however, an inclined
plot oriented towards the south (in the
northern hemisphere) may be of inter-
est, if the greenhouse type chosen
adapts well to the plot, although it
would be difficult to use mechaniza-
tion in such a situation (such as with
low-cost parral greenhouses on coastal
slopes of the south coast of Spain).
Normally, on steep terrains, it would be
preferable to build several separate
greenhouses with their axes parallel to
the contour lines. The evacuation of
rainfall water must be considered,
avoiding it collecting in hollows.
Microclimate of the selected site. There
•
amounts and with the required quality,
for the crop to be cultivated.
Good drainage conditions of the selected
•
plot. This aspect is especially important
in regions of high rainfall. Places with a
high water table must be avoided.
Good soil characteristics for horticul-
•
tural cultivation, either if plants are
going to be cultivated directly in the
soil or if the soil is going to be used to
fill pots or containers.
In the case of greenhouses located near
•
to cities, it is important to evaluate the
air pollution, not just by its incidence
on the plants but also by residues that
may be deposited over the greenhouse,
limiting solar radiation (dust from fac-
tories) or that may be harmful for the
greenhouse cladding material.
Space for future expansion or auxiliary
•
•
should be proper drainage of cold air for
calm nights, and areas that frequently
experience fog should be avoided. The
site should be well illuminated and with-
out shadows (from hills or buildings).
facilities (e.g. a water reservoir for col-
lection of rainfall water or storage of
irrigation water) and buildings (e.g. for
handling or as stores or offices).