Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
B
H
l ¼
ð
3
:
48
Þ
Analogous to susceptibility, the magnetic permeability can be also expressed in
differential terms:
dB
dH
l
0
¼
ð
3
:
49
Þ
Sometimes the term relative permeability is applied. This represents the ratio
between the permeability of the material divided by the permeability of free space
(vacuum, see Eq.
3.14
):
l
l
0
l
r
¼
ð
3
:
50
Þ
It also follows:
l
r
¼ v þ
1
ð
3
:
51
Þ
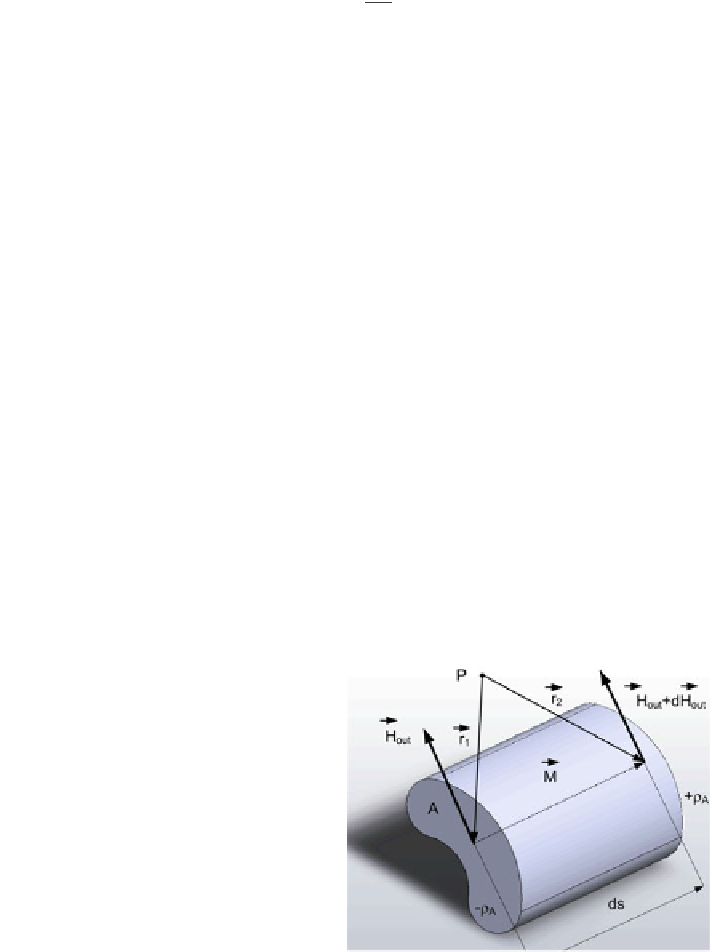
3.1.7 Magnetic Force and Torque on a Dipolar Material
Let us now consider a magnetic material (a soft or hard ferromagnet) that is under
an applied magnetic
eld H
out
. The magnetization vector M is aligned along the
material, as shown in Fig.
3.9
. At each end of the material there exists poles p,
de
ned with the intensity of M as [
12
]:
p
¼
M
A
l
0
¼ q
A
A
ð
3
:
52
Þ
Fig. 3.9 The gradient
magnetic
eld over the
magnetic material


Search WWH ::

Custom Search