Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Now, let us consider Ampere
'
s law [
7
], which states that the magnetic
eld
intensity, measured at a distance r from current I, is proportional to:
/
!
I
r
ð
3
:
4
Þ
For a circular conduit with the closed path
Γ
, and with radius r, Eq. (
3.3
) can also
be written as:
H
ðÞ/
2
p
r
I
ð
3
:
5
Þ
The magnetic
eld that
is generated in this case can be expressed using
Ampere
'
s law as:
I
!
d
l
¼
I
ð
3
:
6
Þ
C
For any closed-loop path, the closed line integral of the magnetic
eld is equal to
the electric current encircled by such a loop.
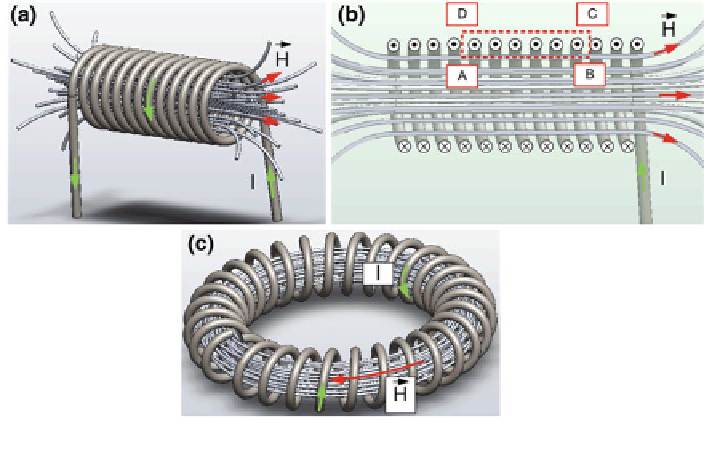
Figure
3.2
a shows a coiled wire wound in several turns (a solenoid) in which the
circulating current produces an almost uniform magnetic
eld. In such a case the
magnetic
eld can also be treated as being parallel with the coil axis (Fig.
3.2
b). For
this particular case we will consider the path given by A
B
C
D in Fig.
3.2
b. Since
-
-
-
Fig. 3.2 a The current-eld relation in a coil and, b a uniform solenoid, where Ampere
'
s law is
applied to the rectangular path A
B
C
-
D
A, c a uniform toroid

Search WWH ::

Custom Search