Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
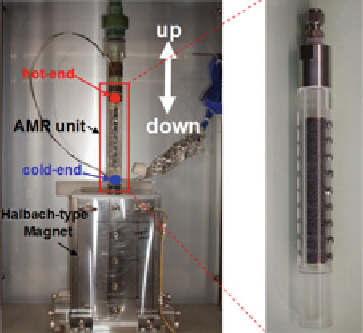
Table 7.3 A reciprocating prototype designed by Toshiba Corporation
Name and address of institute
Corporate Research and Development Center, Toshiba
Corporation 1, Komukai-Toshiba-cho, Saiwai,
Kawasaki, 212-8582, Japan
Name of contact person/email
Akiko Takahashi Saito/aki.saito@toshiba.co.jp
Year of production
2006
Type
Linear
Maximum frequency
1 Hz
Maximum cooling power
N/A
Maximum temperature span
46 K
Type of AMR
Packed bed with spherical particles, (also tested
with parallel Gd plates)
MC material(s)
Gd, Gd alloys, La
Fe
Si based
-
-
Type of magnets
Halbach-type permanent magnet (Nd
-
Fe
-
B)
'
an Jiaotong University presented experimental results on the
operation of the reciprocating magnetic refrigeration prototype in Yu et al. [
16
] and
Gao et al. [
18
]. The testing device consisted of a moving AMR and a water-cooled
electromagnet, which induced a magnetic
Researchers from Xi
uid was
water. In this experiment three different AMRs were tested. The two of those were
packed-bed AMRs,
eld of 2.18 T. The heat-transfer
fl
lled with gadolinium particles with average diameters of 0.3
and 0.56 mm. The masses of the AMRs were 930 and 1,109 g, respectively. The
third AMR consisted of 1,213 g of Gd
Ge particles with average diameters
ranging between 0.3 and 0.75 mm. Using the AMR with Gd particles of 0.3 mm
diameter, a speci
Si
-
-
c cooling power of 20.2 W kg
−
1
at 3 K of temperature span was
obtained. In the case of the AMR
lled with Gd particles with a diameter of
c cooling power was 16.1 W kg
−
1
at a temperature span of 3 K.
The lowest performance was obtained with the Gd
0.56 mm, the speci
Si
Ge-based AMR, where the
-
-
c cooling power was 8.5 W kg
−
1
for a temperature span of 3 K.
speci













Search WWH ::

Custom Search