Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
visual modality during aging, analyzing the performance of the sample (20-70
years range of age). The results showed different ability to elaborate the informa-
tion: in the visuoperceptual test, the Young Group was faster than Junior Group; in
the Verbal Test the Young Group was slower than Adult one. The lack of statistic-
al significant difference between groups and tasks as for accuracy, rule out the role
of the semantic abilities in the time differences. The presence of differences
between groups in the time measure seem to indicate that the ability of use the in-
formation technology depend not only on the age but on modality of task presen-
tation and of execution, too
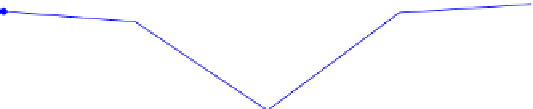
MANOVA: F(8, 450)=2,9794, p=,00291
14
13
v
e
rbal performance
vi
s
ual performance
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
20-29y
30-39y
40-49y
50-59y
60-69y
Groups
Fig. 3
Representation of the verbal and visual performance at the SAT of the 5 groups. The
Y values represent the Msec time.
According to Githens et al. [3], the e-learning in older adults results difference
that of younger and juniors and these difference, probably depend by the interrela-
tion among cognitive and emotive conditions. We suggest that the emotional criti-
cal factors to determine the successful e-learning performance in adulthood could
be related to the self-consciousness of different modality and speed of elaboration
information (verbal vs. visuospatial abilities). It's also to keep in mind, the infor-
mation technology and its applications were early programmed preeminent for
younger population. Recently, the research interesting was focused also on the
influence of the e-learning on quality life in aging and its improvement.











































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search