Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Phase D.
Finally, a manual revision of the generated smart game instances takes
place, where the related visuals (e.g. background illustrations, buttons) are also
specified.
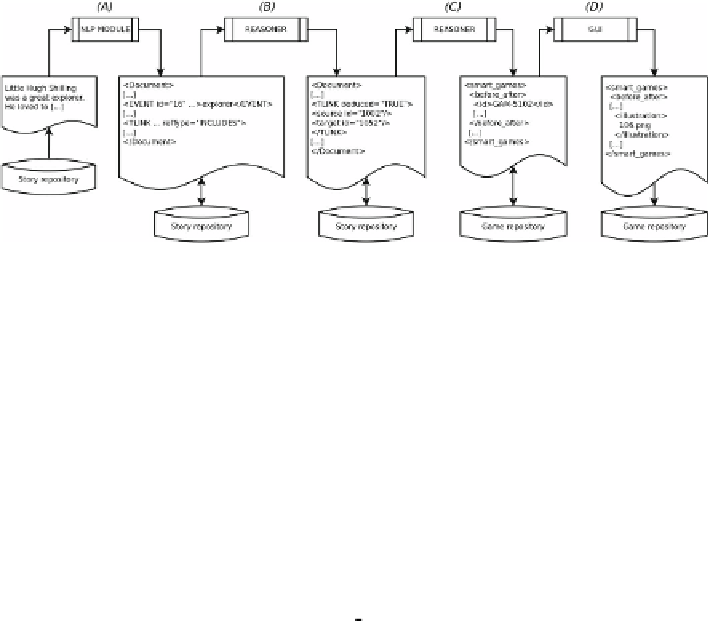
Fig. 2
The smart games generation workflow
It is worth remarking that the errors introduced in the automatic annotation pro-
cess (“Phase A” mentioned above) influence the quality of all subsequent phases.
For instance:
•
badly recognised TLINKs (e.g. a BEFORE relation detected as an AFTER rela-
tion) lead to the deduction of wrong additional relations. Consequently, the smart
games that includes such wrong relations may have temporal games with wrong
solutions marked as correct;
•
poor annotations may:
-
prevent the generation of some classes of games. For instance, without TLINKs
with relation type of INCLUDES/IS INCLUDED/OVERLAPS, the procedure
will not be able to generate any BEFORE/WHILE, WHILE/AFTER, BE-
FORE/WHILE/AFTER smart game;
-
not offer enough alternatives for selecting plausible wrong choices. For
instance, if only one entity is detected in the story, the wrong choices (see dis-
cussion on “Phase C” above) are taken from
other
stories with different char-
acters. However, since these choices are not very much plausible, the quality
of the resulting smart game is reduced.
As a consequence, the manual revision phase takes a crucial importance in the whole
generation process. Understanding the amount of manual effort is then of a major
interest (Sec. 2), since it indicates the overall effectiveness of the automatic approach
used in TERENCE and may give better insight in the tasks that has to be carried out
as priorities (Sec. 3).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search