Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
For the box to move, the cow must push with a horizontal force,
F
C
, equal to the coefficient
of friction multiplied by the weight of the box.
N
C
F g
μ
==
49.05
(3.15)
The work that the cow has done in moving the box, assuming that she only pushes with the
minimum required force, is equal to the applied force times the distance that the box moved.
N-m
WFd
==
98.1
(3.16)
C
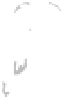
Now let's consider a second example, shown in Figure 3-12, where the cow pulls on a rope
that is attached to the same box. She still must pull the box a distance of 2.0
m
. The angle that
the rope makes with the ground is equal to
q = 30 degrees
. To overcome the friction force, the
cow must apply a horizontal force of 49.05
N
. If she pulls on the rope with a force,
F
C
, the hori-
zontal component of that force will be equal to
F
C
cos30. The force that the cow will have to
exert on the rope to move the box is equal to the friction force divided by cos30.
μ
==
mg
N
F
56.6
(3.17)
C
cos 30
Figure 3-12.
More force is needed to move the box if the force is applied at an angle.
Comparing the situations shown in Figures 3-11 and 3-12, in both cases the cow is performing
the same amount of work. The same horizontal force is applied to move the box the same 2.0
m
distance. However, in the second example the cow has to exert a greater force to perform the
work. Because the rope is at an angle, there is a vertical component to the force the cow exerts
that is wasted in terms of doing horizontal work.
If a force is applied in the direction perpendicular to the motion of an object, then no work
is performed. In Figure 3-12, the vertical component of force exerted by the cow pulling on the
rope does no work because the box does not move in the vertical direction. Another example of
when this situation occurs is with centripetal force. When an object travels in a circle, the
resulting centripetal force is directed inwards perpendicular to the flight path, and because it
is perpendicular to the motion of the object, centripetal force performs no work on the object.
Because work is a force multiplied by a distance, in the SI system of units work will have
units of
N-m
. An
N-m
is also referred to as a
Joule
or
J
for short. A Joule is a unit of energy, and
work and energy are closely related, as we will learn in the next section.