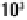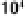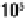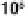Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
The TNT explosion model states that an object will experience the same overpressure from
different explosions if the object is at the same scaled distance from the explosions. For example,
a person standing 10
m
away from a 1000
kg
TNT explosion will experience the same overpressure,
and therefore the same blast damage, as he would if he were standing 1
m
away from a 1
kg
TNT
explosion because the scaled distances for both situations are the same.
The overpressure for a given scaled distance,
Z
, can be estimated from Equation (13.2).
The quantity
p
0
is the overpressure value and
p
a
is the atmospheric pressure, which has a sea-
level value of 101,325
N
/
m
2
. There are three separate square root factors on the bottom of the
right-hand side of Equation (13.2).
⎛
⎞
2
⎛⎞
⎟
Z
⎜
⎟
⎟
⎜
808 1
⎜ +
⎟
⎟
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎟
⎟
⎝⎠
⎟
⎝
4.5
p
p
⎠
0
=
(13.2)
2
2
2
⎛
⎞
⎛
⎞
⎛
⎞
Z
Z
Z
a
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎜
⎜
⎜
1
+
1
+
1
+
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
0.048
⎠
⎝
0.32
⎠
⎝
1.35
⎠
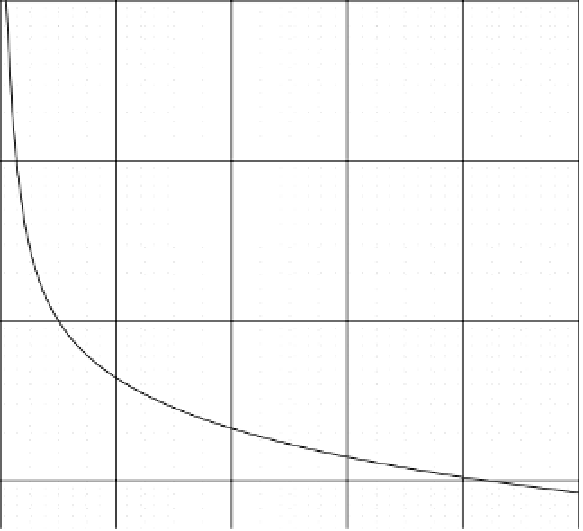
Figure 13-2 displays the overpressure as a function of scaled distance for a TNT explosion.
In comparing the results of Figure 13-2 with the damage values from Tables 13-1 and 13-2,
window breakage will occur when the scaled distance, Z, is equal to approximately 70. A wood-
frame building will collapse at a scaled distance of about 4.2. A person will be knocked over at
a scaled distance of about 10 and will be killed with a 99% probability if the scaled distance is 1.4.
Figure 13-2.
Overpressure as a function of scaled distance, TNT explosion
To summarize, the estimate of the damage to a structure or person from a blast of TNT is
a three-step process: