Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
cavity inside the body. The expanding walls of the temporary cavity can cause very high local
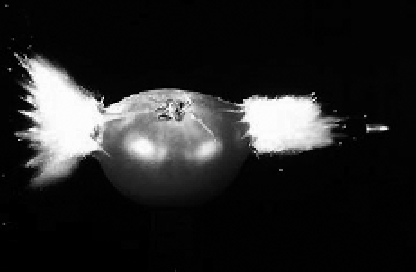
pressures to occur. When a bullet exits an object, such as the tomato shown in Figure 12-1,
damaged tissue is ejected out of the exit hole behind the bullet.
Figure 12-1.
Damage caused by a high-velocity bullet (Photo courtesy of Prof. Andrew Davidhazy,
Rochester Institute of Technology)
The situation is more spectacular (and more disturbing) when a high-velocity bullet passes
through a person's head. Because the skull is solid bone, there is no way to relieve the high
pressures caused by the bullet passing through the head. If the pressure rises to a high enough
level, the head will literally explode. So having a person get thrown backwards when he is shot
is not realistic, but having his head explode when he is shot in the head actually is realistic.
Wounds caused by arrows are less dramatic than those caused by bullets because the
impact velocity is so much lower. Arrows do most of their damage by slicing through arteries
and internal organs. Victims of arrow wounds generally bleed to death. Arrows won't cause
“tail splash,” tissue ejection, or head explosion effects, so don't include them as part of your
arrow game simulation.
Heat Conduction
So far in this topic, the discussions on energy have covered primarily kinetic or potential
energy. There are other forms that energy can take, and one of these other forms is thermal or
heat energy. Thermal energy is related to temperature and will flow from a high-temperature
region to a low-temperature region, similar to the way electricity flows through a wire. There
are several ways that heat energy can be transferred. Heat transfer between a solid and a moving
fluid, such as air blowing over a hot surface, is known as
convective
heat transfer. If the heat is
transferred due to electromagnetic waves emanating from an object, it is known as
radiative
heat transfer. Heat transfer through a solid object is known as heat
conduction
.
Modeling heat conduction can be an important element of a game simulation. For example,
the game may need to model how long it takes a laser to melt its way through the outer skin of
a spaceship or how long it will take for the gas tank of a car that is on fire to explode. The physics
of heat conduction is a rather involved subject, and this section will only provide an introduc-
tion to it, but it will give you the basic information you need to add heat conduction effects to
your games.