Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
geology. The industry has developed specialized software, including Surpac,
GOCAD, Roxar, EarthVision, Petrel, Kingdom, and GeoModeller, to create,
view, and analyze 3D geological models. These modeling tools have become
increasingly powerful, complex, and expensive, leaving an opening for an
easy-to-use, generic tool such as SketchUp.
Part 1: Create Generic Geological Models
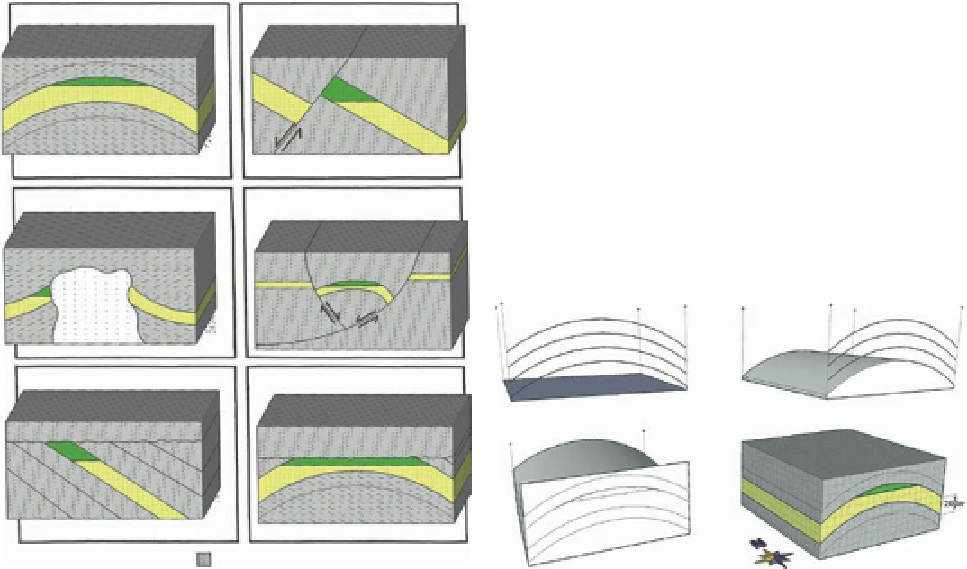
I used SketchUp to create conceptual petroleum trap models that combine
the standard geological features, including sedimentary layers, folds, faults,
unconformities, and piercements, into 3D block models. The resulting models
are exported to the 3D warehouse and viewed in Google Earth and ArcGIS
ArcScene.
Step 1: Create SketchUp Petroleum Trap Models
Goal
: To create generic 3D petroleum trap models.
Inputs
: The CCOP guidelines for risk assessment of petroleum prospects,
by Kalheim, Chaisilboon, and Caluyong (2000).
Tools
: SketchUp, 3D Warehouse, and Google Earth.
To test whether SketchUp could create generic geological models, I created
a set of petroleum trap block models based on the CCOP guidelines. The fold
trap model consists of a 200-m-thick sandstone reservoir with a 100-m-thick
claystones seal and was created using the following
method
A Fold
B Fault
• Createasquarebaseof2000m×2000m
(VCB 2000,20000).
• Createalinecurverepresentingthefold(oruse
shapes.rb to create a 3D dome).
• Copythecurveat100-mintervalstocreatefolds
(VCB 100 × 4).
C Piercement
D Combination fold/fault
E Subunconformity
F Subunconformity
Hydrocarbon accumulation
FiG 15.2
FiG 15.3

Search WWH ::

Custom Search