Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
O
O
O
O
HN
O
O
O
NH
H
3
N
Cl
O
O
NH
O
N
O
N
N
N
N
5
HN
S
N
111
N
In
O
O
O
NH
O
O
O
O
CO OH
O
N
N
N
111
In
COO H
S
N
HO OC
N
Ig G
O
16
17
HO OC
Figure 3.11
Structures of compounds
16
and
17.
The replacement of indium with some other radionuclides would render
these constructs ideal for their application in radiotherapy, although at the
moment, to the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on it.
Ultra-short SWCNTs (US-SWCNTs) were adopted for encapsulating
211
At a
short-life,
α
-emitting radionucleus. The dispersion of this complex in buffer
released a signiicant amount of radionuclide, but after treatment with
chloramine-T or
N
-chlorosuccinimide, leading to the formation of AtCl, the
retention was much higher, with an important overall labelling (At
-
19.6% vs
AtCl 60.7%). There was no direct evidence of At incapsulation into CNTs, but
the authors explored this issue working on I
2
and stated that it is possible to
determine the difference in X-ray-induced Auger emission spectrum due to
physisorbed or included I
2
. From this experiment, the authors revealed the
presence of I
2
signals as evidence of the internal complexation and assumed
that the same preparation obtained using At should give the same results.
These derivatives have not been used for radiotherapy up to now.
55
Also, the possibility of employing CNTs in boron neutron capture therapy
(BNCT) was explored. BNCT is based on the reaction
10
B +
1
n
→
11
B
→
7
Li +
4
He(
α
)
The radiations produced have a very short range in tissues and can
seriously damage DNA. So, to be effective in cancer therapy, the boron has
to be present into cell nuclei with an opportune concentration. Considering
the capacity of CNTs to enter cells and to reach the nuclei, the conjugation
of carborane to nanotubes seems to be a successful strategy to explore. The
appendage of carborane units on SWCNTs was reported by Yinghuai
et al.
56
The
nido
-carboranes were derivatised with an azide and allowed to react with
the double bonds of the CNT skeleton, leading to the formation of aziridine
rings. The derivatives were used in tissue distribution experiments on mice
with transplanted EMT6 mammary cancer cells. When a dimethyl sulphoxide


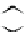
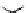
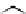
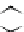

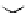
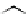

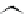






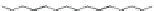






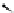
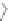












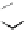





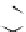

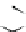
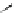
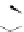


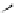



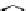
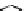




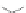
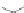









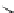
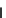













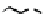






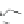

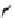




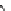



















































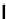

























































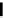




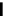
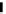
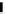























Search WWH ::

Custom Search