Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(10, 0)
CNT
SuperSquare (SS)
CNT
(6, 6)
SuperGraphene (SG)
(9, 0)
CNT
(10,
0
)
SuperCubic (SC)
CNT
CNT
(6, 6)
SuperDiamond (SD)
Figure 9.26
Ordered networks based on CNTs (1D nanostructures). (a, b) Super-
square and super-graphene correspond to 2D networks, whereas (c, d) super-cubic
and super-diamond represent 3D network examples. The four families are constructed
from either armchair or zigzag CNTs in order to study the chirality effects. The red
rings point out the non-hexagonal carbon rings in each node. Figure modiied from
Romo-Herrera
et al
.
164
with permission. See also Colour Insert.
Y and T morphologies were also displayed by the coaxial structures
obtained from the combination of MWCNTs doped with N (MWCNTs-CNx)
as core element, and concentric carbon-based shells formed externally by
pyrolysis of toluene over Fe-coated MWCNTs-CNx.
163
The advantage of this
methodology is that it is possible to control both growth and dimensions of
these nanotube networks, with potential applications in nanoelectronics.

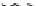





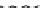
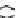
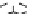
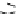
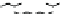


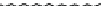


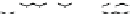































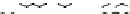

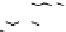


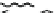

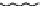
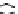

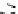




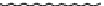











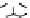
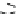




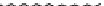



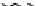
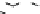


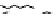

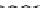
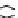
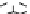
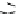


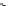






















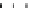








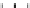













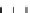





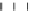


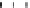














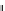















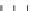























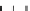

















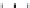



















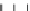

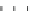





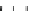










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search