Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
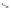
third reaction by exposing the nanotube complexes to Cu
2+
and H
2
O
2
, causes a
pronounced red shift of the (6, 5) nanotube emission, but no corresponding
shift in the (7, 5) band (Fig. 9.22d). Finally, hydroxyl radicals, produced in
the presence of SWCNT by Fe
2+
and H
2
O
2
, damage the DNA backbone and
attenuate emission from both nanotubes but preferentially affect the (7, 5)
emission, without energy shifts (Fig. 9.22e).
HO
a)
O
NH2
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
P
O
O
P
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
O
-
O
O
-
O
O
O
-
O
O
-
O
O
-
O
O
-
N
O
O
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
O
Cl
N
N
O
O
O
O
O
NH
NH
H
H
H
H
O
O
H
2
N
H
2
N
O
O
Alkylating Agent
O
O
O
O
O
O
H
2
O
2
O
O
P
P
O
O
P
O
O
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
-
O
O
O
O
O
-
O
O
O
-
O
O
-
O
-
O
-
O
O
N
N
NH
N
N
N
N
N
O
N
N
O
O
O
O
O
NH
NH
H
H
H
O
H
H
2
N
O
O
H
2
N
O
1
O
2
O
O
O
OH
P
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
O
O
-
O
O
-
O
O
-
O
O
N
N
N
N
N
O
O
O
NH
H
H
O
H
2
N
O
.
OH
Alkylating
Agent
H
2
O
2
1
O
2
(6.5)
(7.5)
980
1,015
1,050
980
1,015
1,050
980
1,015
980
1,015
1,050
1,050
Wavelength (nm)
Wavelength (nm)
Wavelength (nm)
Wavelength (nm)
b) c) d) e)
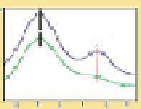
Figure 9.22
Multimodal detection of four reaction pathways. (a) Scheme of
interactions on the SWCNT-DNA complex - an alkylating agent reaction with guanine,
H
2
O
2
adsorption on the nanotube sidewall, a singlet oxygen (
1
O
2
) reaction with DNA,
and hydroxyl radical (•OH) damage to DNA. (b-e) SWCNT-DNA photoluminescence
spectra before (grey) and after introducing the alkylating agent (red) (b), H
2
O
2
(blue)
(c), singlet oxygen (yellow) (d) and hydroxyl radicals (green) (e). Figure redrawn
from Heller
et al
.
137
See also Colour Insert.































































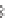


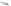



















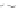














































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search