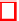
Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
that is
r−
w−p
for
s
). Because
Algorithm 1 is executed on an instance having solutions, we must have
s ∈
U
“good” values of
s
(1 for
s
multiplied by
r−
w−p
. It follows that
ε
(
p,
)=
r−
w−p
/|U|
{eH
T
=
| e ∈S
n
(
0
,w
)
}
. Within our
canviewedasasetof
w
randomly chosen elements of
assumptions, the set
U
}
r
and thus
on average
{
0
,
1
1
(
w
)
1
min
2
r
,
n
w
1
2
r
=2
r
|U|
−
−
≈
from which we deduce the expression (2) of
ε
(
p,
).
Let
W
1
+
W
2
=
{e
1
+
e
2
|
(
e
1
,e
2
)
∈ W
1
× W
2
}
, we also introduce
− ε
(
p,
))
|W
1
+
W
2
|
,
P
(
p,
)=1
−
(1
(3)
the probability of one particular execution of isd loop succeed. Note that within
our assumptions
.
Proposition 1.
For an input
(
H
0
,s
0
)
such that
CSD(
H
o
,s
0
,w
)
|W
1
+
W
2
|
=
|W
1
× W
2
|
=
|W
1
||W
2
|
=
∅
,theAlgo-
rithm 1 will stop after executing
K
0
(
p,
)
+
K
1
|W
1
|
K
2
|W
1
|ε
(
p,
)
+
K
3
2
ε
(
p,
)
≈T
(
p,
)=
(
p,
)
+
(4)
P
P
elementary operations on average.
Proof.
The two leftmost terms are straightforward as the average number of
calls to isd loop is equal 1
/P
(
p,
). One particular execution of (isd 2) will
inspect
|W
1
|
different sums
e
1
+
e
2
and thus succeeds with probability
π
2
=1
−
− ε
(
p,
))
|W
1
|
.
When the parameters are optimal we have
ε
(
p,
)
(1
|W
1
|
1and
thus
π
2
≈ ε
(
p,
)
which accounts for the third term in (4). Finally, if the call
to isd loop fails, the block (isd 3) will be called on average
|W
1
|
|W
1
||W
2
|/
2
times.
Thus if
π
3
is its probability of success, we have (remember
|W
1
+
W
2
|
=
|W
1
||W
2
|
)
− π
3
)
|W
1
||W
2
|
− ε
(
p,
))
2
.
1
−P
(
p,
)=(1
and thus
π
3
=1
−
(1
2
As
ε
(
p,
)2
1, we have
π
3
=
ε
(
p,
)2
and thus the rightmost term of (4).
A consequence of this proposition is that the minimal cost for Algorithm 1
is obtained when
|W
2
|
is maximal (everything else being fixed), that is when
=
k
+
p
.Atthispoint,
|W
1
||W
2
|
(
p,
) is independent of
W
1
and the complexity
is minimal when the two middle terms of (4) are equal, that is when
P
K
2
P
K
1
min
1
k
+
p
K
1
ε
(
p,
)
=
K
2
(
p,
)
|W
1
|
=
L
(
p,
)=
ε
(
p,
)
,
(5)
which is consistent with the results of [14]. We have
WF
ISD
(
n,r,w
)
≈
min
p,
T
(
p,
)