Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2
25
20
1.5
15
1
10
0.5
5
0
0
2.6
1
1.2
1.4 1.6
Fractal dimension,
D
fd
1.8
2
2.2
2.4
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
D
f2
/
D
f1
2.2
2.4
G
H
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0.4
0.6
1
D
f
/
D
fd
,
D
f1
/
D
fd
, and
D
f2
/
D
fd
0.8
1.2
1.4
I
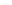
Figure 4.4—Cont'd
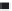
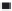
(g) Increase in the dissociation rate coefficient ratio, k
d
with an increase in the fractal dimension
D
fd
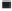
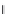
. (h) Increase in the binding rate coefficient ratio, (
k
2
/k
1
) with an increase in the fractal
dimension ratio, D
f2
/D
f1
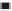
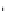
. (i) Increase in the ratio, k/k
d1
, k
1
/k
d
, and k
2
/k
d
with an increase in the
ratio, D
f
/D
fd
, D
f1
/D
fd
, and D
f2
/D
fd
.
¼
The fit is very good. Only three data points are available. The availability of more data points
would lead to a more reliable fit. The binding rate coefficient,
k
1
, exhibits an order of depen-
dence close to one and a half (equal to 1.4928) on the ARC-704 concentration in solution in
the 0-50 nM concentration range.
Figure 4.4b
and
Table 4.3
show the increase in the binding rate coefficient,
k
2
, with an increase
in the ARC-704 concentration (in nM) in the 0-50 nM range in solution for a dual-fractal analy-
sis. For the data shown in
Figure 4.4b
, the binding rate coefficient,
k
2
, is given by:
0
:
4528
0
:
2043
Þ
The fit is very good. Only three data points are available. The availability of more data points
would lead to a more reliable fit. The binding rate coefficient,
k
2
, exhibits an order of depen-
dence less than one-half (equal to 0.4528) on the ARC-704 concentration in solution in the
0-50 nM concentration range.
k
2
¼ð
3
:
3348
0
:
877
Þ½
ARC
704, nM
ð
4
:
5b