Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3
1
2.5
0.8
2
0.6
1.5
0.4
1
0.2
0.5
0
0
0
500
1000
Time (s)
1500
2000
2500
0
500
1000
Time (s)
1500
2000
2500
B
A
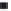
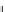
Figure 16.12
Binding of complementary ss DNA to a molecular beacon. Influence of different immobilization
techniques (
Li et al., 2001
): (a) Streptavidin-biotin, (b) BSA-streptavidin-biotin. When only a solid
line (--) is used then a single-fractal analysis applies. When both a dashed (- - -) and a solid (--)
line are used then the dashed line represents a single-fractal analysis and the solid line represents a
dual-fractal analysis.
Figure 16.12b
shows the binding of 50 nM complementary target 5
0
-GCG ACC ATA GCG
ATT TAG (A-3
0
) in solution to the MB (5
0
-TMR-CCT AGC TCT AAA TCG CTA TGG
TCG CGC (biotin dT)AG G-DABCYL-3
0
) immobilized using BSA-streptavidin-biotin
immobilized on a biosensor surface (
Li et al., 2001
). Once again, a dual-fractal analysis is
required to adequately describe the binding kinetics. The values of (a) the binding rate coef-
ficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis, and (b) the binding rate
coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a dual-fractal analysis are
given in
Table 16.8
and
Table 16.9
.
It is of interest to note that when one compares the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, for a dual-
fractal analysis when streptavidin-biotin is used with when BSA-streptavidin-biotin is used,
both of the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
are higher when BSA-streptavidin-biotin is used.
Figure 16.13a
shows the binding of 50 nM complementary oligonucleotide target (5
0
-GCG
ACC ATA GCG ATT TAG(A-3
0
) in solution to the MB immobilized on the biosensor sur-
face by BSA-streptavidin-biotin (
Li et al., 2001
). A dual-fractal analysis is required to ade-
quately describe the binding kinetics. The values of (a) the binding rate coefficient,
k
, and
the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis, and (b) the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a dual-fractal analysis are given in
Tables 16.10
and
16.11
.
Figure 16.13b
shows the binding of 50 nM one base mismatch oligonucleotide target
(5
0
-GCG ACC ATA TCG ATT TAG(A-3
0
) in solution to the MB immobilized on the biosen-
sor surface by BSA-streptavidin-biotin (
Li et al., 2001
). Once again, a dual-fractal analysis is
required to adequately describe the binding kinetics. The values of (a) the binding rate coef-
ficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis, and (b) the binding rate