Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
concentration in solution in the 20-60 nM range as noted by the dependence between one and
one and a half (equal to 1.307) order exhibited.
Martinez et al. (2009)
recently pointed out that DNA/RNA-based analytical methods are
important in molecular biology, disease diagnosis, and gene expression. They emphasize
that biosensors are popular as they permit the detection of a large number of samples using
a fast and simple setup. Biosensors permit the real-time detection of nucleic acid molecules
and gene expression changes (
Feng et al., 1999; Steel et al., 2000; Steemers et al., 2000;
Broude et al., 2001; Preininger and Chiarelli, 2001; Culha et al., 2004; Gang et al., 1999
).
Martinez et al. (2009)
explain the importance of efficiency, reproducibility, and the stable
immobilization of the DNA probes onto specific surfaces.
Martinez et al. (2009)
report that their design of a new MB biosensor overcomes the previous
limitations of MBs for surface immobilization. In essence, their new design adds LNAs to the
beacon structure, resulting in a LNB that exhibits robust stability after surface immobiliza-
tion. They indicate that their LNB-based biosensor exhibited better stability, reproducibility,
selectivity, and robustness when compared with the regular molecular beacons (RMBs).
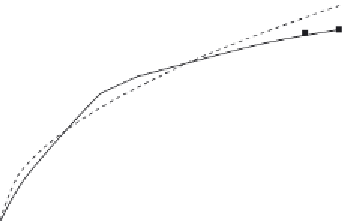
Figure 16.6
shows the binding of 10
m
M of the target to the LNB-based biosensor. A dual-
fractal analysis is required to adequately describe the binding kinetics. The values of
(a) the binding rate coefficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis,
and (b) the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a
dual-fractal analysis are given in
Table 16.4
.
It is of interest to note that as the fractal dimension increases by a factor of 1.67 from a value
of
D
f1
equal to 1.406 to
D
f2
equal to 2.3538, the binding rate coefficient increases by a factor
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0
2
4
Time (min)
6
8
10
Figure 16.6
Binding of 10 mM target to LNA (locked nucleic acid bases) molecular beacon
(
Martinez et al., 2009
). When only a solid line (--) is used then a single-fractal analysis applies.
When both a dashed (- - -) and a solid (--) line are used then the dashed line represents a
single-fractal analysis and the solid line represents a dual-fractal analysis.