Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
20000
14000
12000
15000
10000
8000
10000
6000
4000
5000
2000
0
0
0
50
100
Time (s)
150
200
0
50
100
Time (s)
150
200
A
B
20000
15000
10000
5000
0
0
50
100
150
200
C
Time (s)
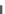
Figure 16.2
Binding of 40 nM FAM-SP-2
1 mM ATP, pH 8.0, to the singly labeled DNA
hairpin smart probe (
Song and Zhao, 2009
). Influence of
þ
5.6 nM/s 4TPNK
þ
exonuclease units: (a) 0.5, (b) 1.0,
(c) 2.5. When only a solid line (--) is used then a single-fractal analysis applies. When both a
dashed (- - -) and a solid (--) line are used then the dashed line represents a single-fractal analysis
and the solid line represents a dual-fractal analysis.
l
The values of (a) the binding rate coefficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-
fractal analysis, and (b) the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a dual-fractal analysis are given in
Table 16.2
.
It is of interest to note that as the fractal dimension increases by a factor of 1.475 from a
value of
D
f1
equal to 0.822 to
D
f2
equal to 1.213, the binding rate coefficient increases by
a factor of 1.89 from a value of
k
1
equal to 58.33 to
k
2
equal to 110.31. The changes in
the binding rate coefficient and in the degree of heterogeneity or the fractal dimension on
the biosensor surface are in the same direction.
Figure 16.2b
shows the binding of 40 nM FAM-SP-2
þ
5.6 nM/s 4T PNK
þ
1 mM ATP and
1.0 units of
exonuclease at pH 8.0 to the singly labeled DNA hairpin smart probe (
Song and
Zhao, 2009
). Once again, a dual-fractal analysis is required to adequately describe the bind-
ing kinetics. The values of (a) the binding rate coefficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
,
for a single-fractal analysis, and (b) the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal
dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a dual-fractal analysis are given in
Table 16.2
.
l