Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
is an extremely potent peptide cytokine that serves as an endogeneous mediator of inflamma-
tory, immunodefense, and host-defense functions (
Old, 1987
).
DeKossodo et al. (1995)
report
that elevated concentrations of TNF in serum indicate a broad series of pathogenic states such
as neonatal listeriosis, severe meningococcemia, HIV infection, systemic erythema nodosum
leprosum, endotoxic shock, graft rejection, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Wang et al. (2006)
emphasize that sensitive detection methods are required to help detect this trace biomarker
to promote the understanding of tumor biological processes and inherent mechanisms, and
discover drugs that have a therapeutic potential for the treatment of diseases.
College Hill (2009)
in the journal Nature defines biomarkers, and as stated in the beginning
of the chapter, “as valuable tools used across the biological science spectrum. These tools are
used both in research and in diagnostics as indicators of normal and disease processes or to
assess pharmacologic response.” Some of the more recent methods used to detect TNF-
a
include ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay;
Yates et al., 1999
;
Rossomando and
White, 1993
), radioimmunoassay (
Teppo et al., 1987
), and fluorescence immunoassay
(
Okubo et al., 1998; Cesaro-Tadic et al., 2004
) and by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain
reaction (
Takahashi et al., 2001
).
Wang et al. (2006)
report that the electrochemical technique is useful in detecting bio-
markers, because of its high sensitivity, inherent simplicity, miniaturization, and cost. The
detection techniques mentioned in the previous paragraph, (
Wang et al., 2006
) are either
hazardous to health, time-consuming and labor intensive or require highly qualified and sophis-
ticated personnel. These authors have developed poly(guanine) (poly[G])-functionalized silica
NPs and mediator-induced catalytic oxidation of guanine for an amplified EIA of TNF-
a
.
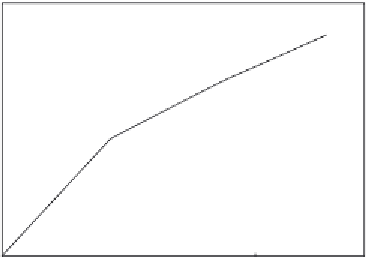
Figure 15.2
shows the binding of 1.0 ng/ml TNF-
a
in 0.1 M PBS buffer containing Ru(bpy)
3
Cl
2
to poly(guanine) functionalized nanoparticles (NPs;
Wang et al., 2006
). A single-fractal
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
10
20 30
Time (min)
40
50
Figure 15.2
Binding of tumor necrosis factor (TNF-
) using poly(guanine) functionalized silica nanoparticles
(NPs;
Wang et al., 2006
).
a