Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
800
1000
600
800
600
400
400
200
200
0
0
0
20
40
Time (s)
60
80
100
0
20
40
Time (s)
60
80
100
A
B
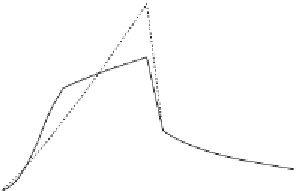
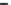
Figure 14.6
Binding and dissociation of alcohol vapors exposed for 36 and 24 h to an ethanol sensor (TFE-850)
(
Pokhrel et al., 2007
): When only a solid line (--) is used then a single-fractal analysis applies.
When both a dashed (- - -) and a solid (--) line are used then the dashed line represents a
single-fractal analysis and the solid line represents a dual-fractal analysis, and the dashed line
represents the single-fractal analysis. In both cases, the solid line is the best fit line.
analysis is required to describe the binding and the dissociation kinetics. The values of (a) the
binding rate coefficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis, and
(b) the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a
dual-fractal analysis, (c) the dissociation rate coefficient,
k
d
, and the fractal dimension,
D
fd
,
for a single-fractal analysis, and (d) the dissociation rate coefficients,
k
d1
and
k
d2
, and the
fractal dimensions
D
fd1
and
D
fd2
, for a dual-fractal analysis are given in
Tables 14.4
and
14.5
.
The estimated value of the fractal dimension in the binding phase is zero. This indicates that
the TFE-850 sensor surface acts like a Cantor-like dust (
Viscek, 1989
). It is of interest to note
that as the fractal dimension in the dissociation phase increases by a factor of 3.19 from a
value of
D
fd1
equal to 0.8036 to
D
fd2
equal to 2.5608, the dissociation rate coefficient
increases by factor of 14.56 from a value of
k
d1
equal to 9.8028 to
k
d2
equal to 142.27. Note
that changes in the fractal dimension or the degree of heterogeneity on the TFE-850 ethanol
sensor surface in the dissociation phase and in the dissociation rate coefficient are in the same
direction.
Figure 14.6b
shows the binding and dissociation kinetics observed when thee TFE-850 etha-
nol sensor was exposed for 24 h to alcohol vapors. A dual-fractal analysis is required to
describe the binding kinetics. A single-fractal analysis is adequate to describe the dissociation
kinetics. The values of (a) the binding rate coefficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a
single-fractal analysis, and (b) the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal
dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a dual-fractal analysis, and (c) the dissociation rate coefficient,
k
d
, and the fractal dimension,
D
fd
, for a single-fractal analysis are given in
Tables 14.4
and
14.5
.