Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.9
1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
Fractal dimension,
D
f
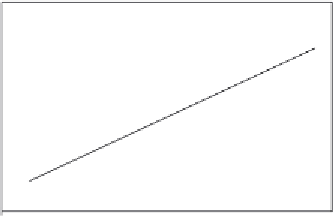
Figure 9.10
Increase in the binding rate coefficient, k with an increase in the fractal dimension, D
f.
first- (equal to 0.816) order of dependence on the fractal dimension,
D
f
, or the degree of het-
erogeneity that exists on the sensor chip surface.
9.4 Conclusions
A fractal analysis is presented for the binding and the dissociation (if applicable) of (a) dif-
ferent bradykinin concentrations (in nM) in solution to bradykinin B
2
receptors immobilized
on a RWG biosensor surface (
Fang et al., 2006
), (b) m
b
CD cholesterol to HeLa cells
cultivated on a gold-coated prism surface (
Ziblat et al., 2006
), and (c) a calcium
þ
FRET-
based calcium biosensor employing troponin C. TN-XL fluorescence observed was observed
in vivo
in this case (
Mank et al., 2006
). Both single-and dual-fractal analysis were used.
The dual-fractal analysis was used only when the single-fractal analyses did not provide an
adequate fit. This was done using
Corel Quattro Pro 8.0 (1999)
.
The fractal dimension provides a quantitative measure of the degree of heterogeneity present
on the biosensor chip surface. The fractal dimension for the binding and the dissociation
phase,
D
f
and
D
fd
, respectively, is not a typical independent variable, such as analyte concen-
tration, that can be directly manipulated. It is estimated from
Equations (9.1)-(9.3)
, and one
may consider it as a derived variable.
An increase in the fractal dimension value or the degree of heterogeneity on the biosensor
surface leads, in general, to an increase in the binding rate coefficient. For example, for
the binding of different bradykinin concentrations in solution in the 8-128 nM range (
Fang
et al., 2006
), and for a dual-fractal analysis the binding rate coefficient,
k
2
, exhibits a
6.571 order of dependence on the fractal dimension,
D
f2
, or the degree of heterogeneity that
exists on the biosensor surface. This indicates that, in this case at least, the binding rate coef-
ficient,
k
2
, is very sensitive to the fractal dimension or the degree of heterogeneity present on
the biosensor chip surface.