Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
2.8
2.9
Fractal dimension,
D
f2
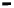
Figure 8.3
Increase in the binding rate coefficient, k
2
, with an increase in the fractal dimension, D
f2
.
The fit is good. Only three data points are available. The availability of more data points would
lead to a more reliable fit. The binding rate coefficient,
k
2
, is very sensitive to the degree of het-
erogeneity or the fractal dimension,
D
f2
, that exists on the QCM sensor surface as indicated by
the order of dependence between five and a half and six (equal to 5.667) exhibited.
Masson et al. (2007)
point out the need to quantitatively measure the expression of biological
markers to better understand their roles in disease progression. The measurement of
biological markers in serum is difficult primarily because of the nonspecific adsorption of
serum proteins.
Battaglia et al. (2005)
have indicated that the stability of SPR biosensors
was improved in a cell culture media during the direct measurement of biomarkers for wound
healing by using a coating of
N
-hydroxysuccinimide-activated 16-mercaptohexadecanoic
acid (NHS-MHA).
Masson et al. (2007)
have extended this concept to measure the
biomarkers of myocardial infraction (MI) in undiluted serum by using NHS-MHA as a non-
fouling coating on a SPR biosensor surface.
Masson et al. (2004, 2005
) have shown that non-
specific binding in SPR biosensors may be reduced as a result of the recent developments in
surface coatings used for SPR biosensing surfaces. These coatings permit the reduction of
nonspecific binding while simultaneously improving the specific signals. This is achieved
by increasing the number of antibodies on the gold surface of the SPR biosensor.
Myoglobin (MG) and cardiac troponin I (cTnI) are two MI markers.
Masson et al. (2007)
have detected MG in undiluted serum without sample pretreatment using the SPR biosensor.
Figure 8.4
shows the binding of 50 ng/mL myoglobin in solution to antimyoglobin anti-
body immobilized on a SPR biosensor surface. A dual-fractal analysis is required to ade-
quately describe the binding kinetics. The values of (a) the binding rate coefficient,
k
, and
the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis, and (b) the binding rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a dual-fractal analysis are given in