Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
300
250
250
200
200
150
150
100
100
50
50
0
0
0
5
10
15
Time (min)
20
25
30
0
5
10
15
Time (min)
20
25
30
B
A
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
5
10
15
Time (min)
0
20
25
30
C
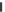
Figure 8.2
Binding of different antigens in solution to the anti CD7, anti CD5, and anti CD3, antibody,
respectively immobilized on the Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) surface (Zeng et al., 2006):
(a) CD7 (b) CD5 (c) CD3. When only a solid line (—) is used then a single-fractal analysis applies.
When both a dashed (- - -) and a solid (—) line are used then the dashed line represents a single-
fractal analysis and the solid line represents a dual-fractal analysis.
coefficient,
k
, and the fractal dimension,
D
f
, for a single-fractal analysis, and (b) the binding
rate coefficients,
k
1
and
k
2
, and the fractal dimensions,
D
f1
and
D
f2
, for a dual-fractal analysis
are given in
Table 8.1
. It is of interest to note that as the fractal dimension increases by a fac-
tor of 2.27 from a value of
D
f1
equal to 1.0768 to
D
f2
equal to 2.4426 the binding rate coef-
ficient increases by a factor of 4.63 from a value of
k
1
equal to 10.081 to
k
2
equal to 46.636.
It is seen that, once again, changes in the degree of heterogeneity or the fractal dimension on
the QCM surface and in the binding rate coefficient are in the same direction.
Figure 8.3
and
Table 8.1
show for the binding of the different CD antigens, CD1, CD3, and CD5
in solution to their corresponding antibodies, anti-CD3, anti-CD5, and anti-CD7, respectively,
and immobilized on a QCM biosensor surface, the increase in the binding rate coefficient,
k
2
,
with an increase in the fractal dimension,
D
f2
. The binding rate coefficient,
k
2
, is given by:
D
5
:
667
2
:
637
k
2
¼ð
0
:
394
0
:
178
Þ
ð
8
:
2
Þ
f2