Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1600
800
1400
1200
600
1000
800
400
600
200
400
200
0
0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0
200
400
Time (s)
600
800
A
Time (s)
B
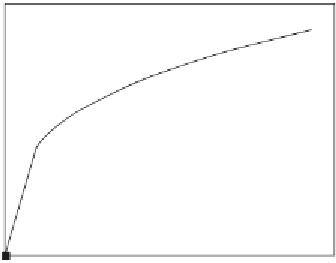
Figure 6.3
(a) Binding of 40 ppm antithrombin in solution to the immobilized biotinylated thrombin on a
CMB chip. (b) Binding of 20 nM thrombin in solution to the immobilized biotinylated aptamer on
a CMB chip (
Centi et al., 2008
).
Table 6.2: Binding of (a) 40 ppm antithrombin antibody to the biotinylated thrombin
immobilized on a CMB chip (
Centi et al., 2008
), (b) 20 nM thrombin in solution to an
immobilized biotinylated aptamer on a CMB chip (
Centi et al., 2008
), and (c) binding and
dissociation of 60 nM thrombin in solution to an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)
biosensor (
Li et al., 2008
).
Analyte in Solution/
Receptor on Surface
k
k
d
D
f
D
fd
References
40 ppm antithrombin/
biotinylated thrombin
on CMB chip
83.044
1.593
na
2.3862
0.0182
na
Centi et al.
(2008)
20 nM thrombin/
biotinylated aptamer
immobilized on a CMB
chip
7.9747
0.424
na
1.4424
0.03892
na
Centi et al.
(2008)
60 nM thrombin/EIS
biosensor
122.88 15.23 95.145 22.52 1.810 0.1696
1.716
0.264
Li et al.
(2008)
Li et al. (2008)
report that antibodies have been widely used as biological recognition
elements in biosensors. However, they do have limitations such as their production
in vivo
,
limited target analytes, limited shelf life, as well as being subject to thermal denaturation
(
O'Sullivan, 2002
). O'Sullivan et al. (1997) point out that aptamers may be used as biological
recognition elements for drugs, enzymes, peptides, and proteins.
Ho and Leclerc (2004) and
Pavlov et al. (2004)
point out that aptamers have been used in optical biosensors.