Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
N
H
N
O
O
O
O
H
N
X
N
N
N
N
HO
H
dansyl
O
O
O
O
O
N
R
1
R
1
R
1
R
1
HN
NH
HN
NH
O
R
1
O
O
R
2
R
2
O
O
29
R
2
R
2
X = NH
HN
O
HN
NH
NH
HN
O
O
O
O
30
R
2
X = O
NH
R
3
R
3
R
3
R
3
R
3
H
2
N
NH
2
H
2
N
NH
2
O
28
31
H
2
N
AA
1-3
= Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Ser, Pro, Asp, Tyr, His, Lys, Gln, Phe
12 × 12 × 12 = 1,728 receptors
Fig. 8 Schematic illustration of receptor library 28 with an additional hydrocarbon chain. Side
chains consist of three variable amino acids AA
1-3
. The substrates
D
-Ala-
D
-Ala 29 and
D
-Ala-
D
-
Lac 30 were labeled with a dansyl fluorescence marker. An additional arm attached to the
hydrocarbon chain gave library 31
receptors, 21, consisting of two identical peptidosulfonamide side chains, were
bridged by several templates 22-27. These scaffolds differed in both their flexibility
and the distance between the amine groups. A dye-label enabled screening of a
tripeptide library containing 29
3
24,389 members (14). The highest overall
binding affinity in chloroform was found for the scaffold 22, with a binding
constant for the peptide
D
-Ala-
L
-Asp-
D
-Ser of 4
¼
10
3
M
1
. Since no binding
affinity could be observed for a one-armed analog, it was concluded that the second
arm is necessary for efficient tripeptide binding. The second best receptors, with
binding constants of up to 8
10
2
M
1
, were those with template 23, which is
more rigid and offers less space between the two arms. Third ranked are the two
scaffolds 24 and 25. The distance between side chains seems to be too large in these
two cases for stable complexation of the peptidic substrates.
When implementing 26 as linker, the corresponding receptor showed high
selectivity (
95%) for the amino acid sequence Glu-His-X. However, the binding
affinity was rather poor—this was again probably due to the large distance between
the two arms. No affinity at all could be observed for 27. The cause for this effect
can probably be found in the repulsion between the free electron pairs of the
sulfonamide oxygen groups, which would be in too close proximity in the depicted
chair-chair conformation of the template. Instead, it adopts a boat-chair conforma-
tion which results in the loss of tweezer structure. A common feature of all
examined host systems in this work is the high guest selectivity: the amino acid
AA
1
is almost always an acid; AA
2
is a polar amino acid such as asparagine or
histidine. For the residue at position AA
3
, which is bound directly to the resin, no
tendency could be observed.
The binding studies of library 21 were again only conducted in organic solvents.
For further studies in aqueous solution, two more combinatorial tweezer libraries
(28, Fig.
8
) each consisting of 1,728 members were synthesized, based on the best
scaffold 22 [
20
]. As before, the two arms were identical but instead of
sulfonamides, they now consisted of tripeptides, to facilitate the combinatorial
>

































































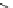































Search WWH ::

Custom Search