Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
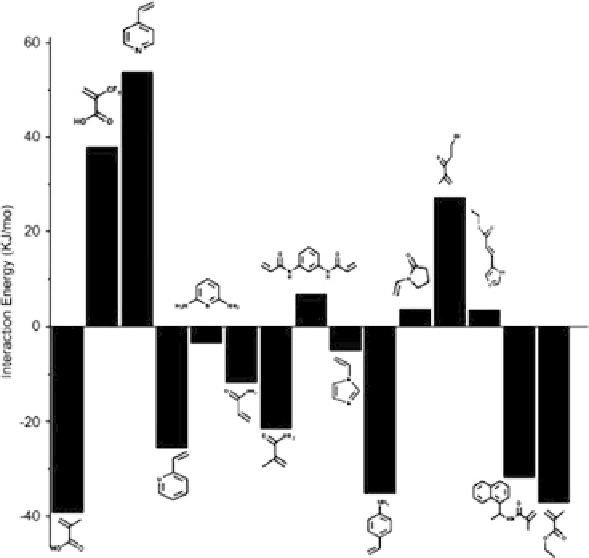
Fig. 6 (continued)
Pavel and Lagowski [
65
,
98
,
162
] studied the intermolecular interactions in
molecular imprinting of theophylline (THO). The minimized structures of five
ligands, THO and its derivatives (theobromine, theophylline-8-butanoic acid, caf-
feine and theophylline-7-acetic acid) were employed in MD simulation using
Cerius2 version 4.10 software designed by Accelrys, Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA).
The polymer consistent force field (PCFF) was employed, as it was found to be very
suitable and reliable for the molecular simulation of organic molecular clusters of
monomers and polymers [
163
-
165
]. The forces acting on each atom of a model
polymer were calculated. The initial molecular clusters of the simulated monomers
and polymers were optimized, giving information about total energies (
E
), energy
differences (DE), and distances (
d
) between the monomers and different ligands in
a given cluster. Using the same MD simulations, Pavel et al. [
65
] designed
monomers for MIPs specific for chemical warfare agents. They showed successful
predictions of interaction energies, the closest approach, distances, and the active
site groups.
Several research groups have used the PM3 method for the analysis of
template-functional monomer complexes [
166
]. From a computational perspective,
PM3 provides improved modeling of non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen-
bonding and van der Waals interactions.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search