Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
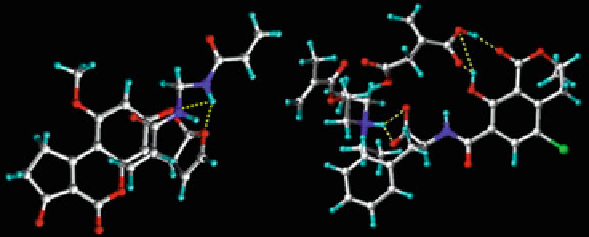
Fig. 3 3D molecular complex between negatively charged OTA and functional monomers
DEAEM (
left
); 3D molecular complex of AFB1 with MBAA functional monomer (
right
) (oxygen
atoms are shown in
red
, carbon atoms are
white
and the
light blue
atoms are hydrogen).
Reproduced with permission [
86
]
The same team also synthesized MIPs capable of the controlled release of
simazine in water [
82
]. Leapfrog was used to identify a list of monomers used in
the production of polymers with different affinities and correspondingly different
release profiles of the herbicide. The speed of release correlated with the calculated
binding characteristics. The high affinity, MAA-based polymer released ~2% and
the low-affinity HEMA-based polymer released ~27% of the template over 25 days.
In an interesting study, computationally designed methacrylate-based synthetic
polymers that inhibit QS by sequestering the bacterial signal molecules were
developed by Piletska et al. Biofilm production and expression of virulence factors
were correlated with Quorum Sensing (QS), a density-dependent regulation of gene
expression controlled by specific signal molecules produced by bacteria. The
polymers were able to absorb 0.1-0.3 mg (per gram of polymer) of
N
-acyl-
homoserine lactones (AHLs). This work has implications in aquaculture, where
these polymers can sequester a (a test bacterium) signal molecule of
Vibrio fischeri
and prevent QS-controlled phenotypes,
thus representing a new solution for
controlling disease outbreaks [
85
].
Polymers with affinity to two of the most abundant mycotoxins AFB1 and OTA
were designed by the computational approach (Fig.
3
) for application in the
ToxiQuant T1 System (TQT1). The principle of quantification of AFB1 and OTA
using the TQT1 instrument consisted of fluorimetric analysis of mycotoxins
adsorbed on the polymer upon exposure to UV light. High affinity of the resins
allowed the adsorption of both toxins as discrete bands on the top of the cartridge
with detection limit as low as 1 ng of mycotoxin. Based on the computational
modeling, MBAA was selected for the preparation of the polymer specific for
AFB1, and a mixture of DEAEM and IA was selected for preparation of a polymer
specific for OTA. DMF was used as the porogen in both cases [
86
].
A similar method was previously employed to prepare an MIP with high affinity
for nonylphenol, a xenobiotic used in the manufacture of antioxidants, lubricating oil
additives, and surfactants (Table
2
). Nonylphenol is degraded in wastewater plants
leading to the formation of lipophilic nonylphenol derivatives [
87
]. Chromatographic
Search WWH ::

Custom Search