Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
BARNAE
Input block(prior to
segmentation)
Elimination analysis
Entropy Based
Edge Detection
Gray level intensity of
interest identification
Restoration analysis
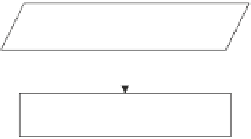
Fig. 3.21
The main components in the bounded-area restoration and non-bounded area
elimination
procedures are discussed below using two instances of hand bone radiographs. The
first image illustrated the elimination procedure whereas the second image illus-
trated the restoration procedure.
The entire restoration and elimination scheme can be clearly illustrated using
the flowchart in Fig.
3.21
which shows the scheme is using input of detected edges
on the pixels that is of identified gray level intensity of interest. The intensity of
interest identification is discussed in
Sect. 3.5.1
; the entropy based edge detection
is discussed in
Sect. 3.5.2
; the BARNAE algorithm is discussed in
Sect. 3.5.3
.
3.5.1 Gray Level Intensity of Interest Identification for
Elimination
The purpose to identify the range of pixel intensity is to reduce the number of pix-
els that requires further analysis, only pixels that are in high risk of wrongly clas-
sified are proceed to analysis to serve two goals to determine whether to remain
the pixel or eliminate it as segmented pixel (elimination in this context means set-
ting the corresponding pixel to intensity 0).
Firstly, the histogram of the segmented bone pixels is plotted and interpolated
using curve fitting technique by a sum of multiple Gaussian models:
−(
x
−
x
i
)
2
2
e
i
n
=
3
(3.63)
g
(
x
) =
A
i
e
i
=
1
The parameter n is set as 3 as there are 3 groups of pixels which comprise of a
group of compact bone pixels, a group of background pixels, and a group of pixels
which belong to either soft-tissue region or spongy bone region. Next, to find the
third group of pixels, the second and third inflection points are obtained and the
pixels within these two limits are classified as the targeted group of pixels which
would be analyzed to perform the restoration and elimination.











Search WWH ::

Custom Search