Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
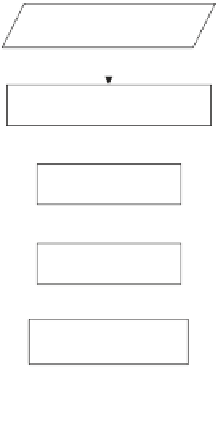
Fig. 3.9
The proposed
automated anisotropic
diffusion
Input Image
Parameter-free diffusion
function
8 Directions
∆
t setting as 1/7
Automated scale
selection
End
3.4 The Proposed Adaptive Crossed Reconstruction (ACR)
Algorithm Design
The segmentation system begins with loading a digital radiograph of hand skeletal
bone into the software. Prior to the core phase of the designed adaptive crossed
recombination system, the input image is the outcome of image afer being pro-
cessed by a series of pre-processing such as histogram equalization and aniso-
tropic diffusion; the purpose of the former implementation is to standardize the
radiograph so that radiographs from different machine of x-ray will be standard-
ized; the purpose of the latter implementation is to enhance the histogram graph
by diffusing the intensity value within the bone while preserving the sharp edge of
the bone.
After the pre-processing, the image will enter the main phase of segmentation.
The algorithm begins with division accordingly to quadruple division algorithm in
Sect. 3.4.2
. The purpose of dividing the image into sub-image is to fulfil adaptive
property; the image contrast is not uniform and the degree of changes is increased
throughout the whole image from the phalange until the carpal. Dividing the
image into sub-image is able to resolve this problem by providing a suitable envi-
ronment for subsequent step of k-mean clustering. Henceforth, the divided sub-
image is termed as block.
The k-mean clustering is performed on each block. With the k-means unsuper-
vised clustering technique, the x-ray image is clustered into two and three groups
which represent bone, soft-tissue region and bone, soft-tissue region and back-
ground with 'k' value equals to two and three respectively. The implementation








Search WWH ::

Custom Search