Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
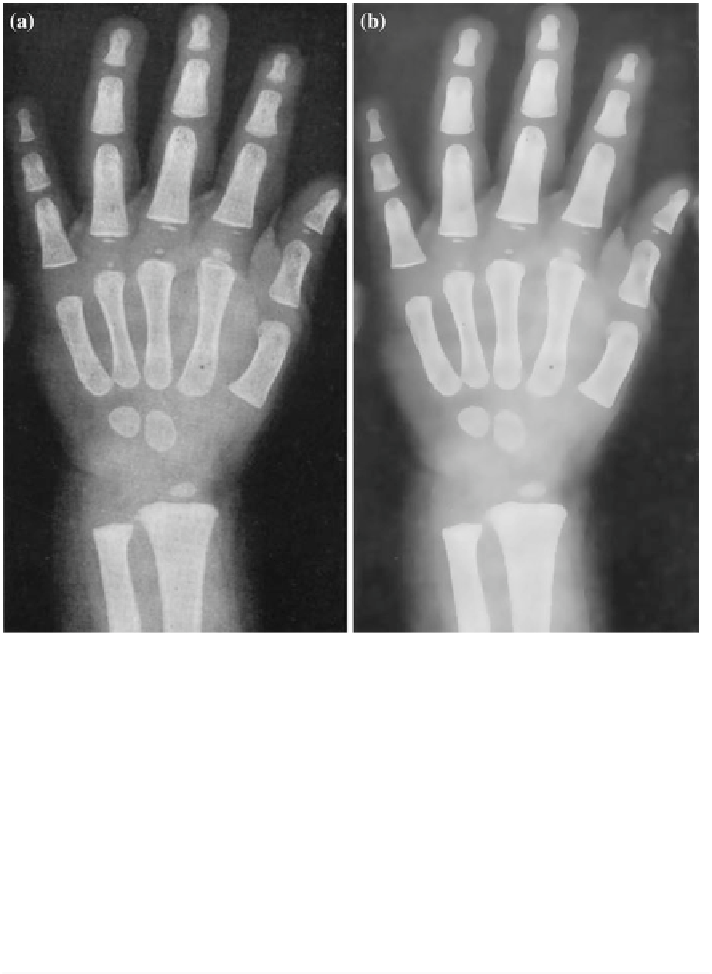
Fig. 4.2
The radiograph is diffused by different algorithm for comparison.
a
Original image.
b
Gaussian filter.
c
Average filter.
d
Wiener filter.
e
Symmetric Nearest Neighbor (
SNN
) filter.
f
Anisotropic diffusion
Table 4.1
Comparison of expected image homogeneity of different age group before and after
the anisotropic diffusion processing
Age group
Image homogeneity
Image homogeneity
Before anisotropic diffusion
After anisotropic diffusion
0-2
0.7056
0.8235
3-6
0.6984
0.8245
7-9
0.7132
0.8365
10-12
0.7189
0.8423
13-15
0.7028
0.8212
16-18
0.6927
0.8234
the edge has not been diffused and thus details are retained. Edges of structures, thus,
are intensified to facilitate identification. Moreover, the anisotropic diffusion is able to
manipulate the intensity and direction of diffusion to prevent diffusion across the edges;
instead it enables diffusion in direction parallel along the edges; therefore, edges are
preserved and are enhanced simultaneously. This is important in distinguishing the ana-
tomical structures outlines in medical image processing.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search