Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
13.7
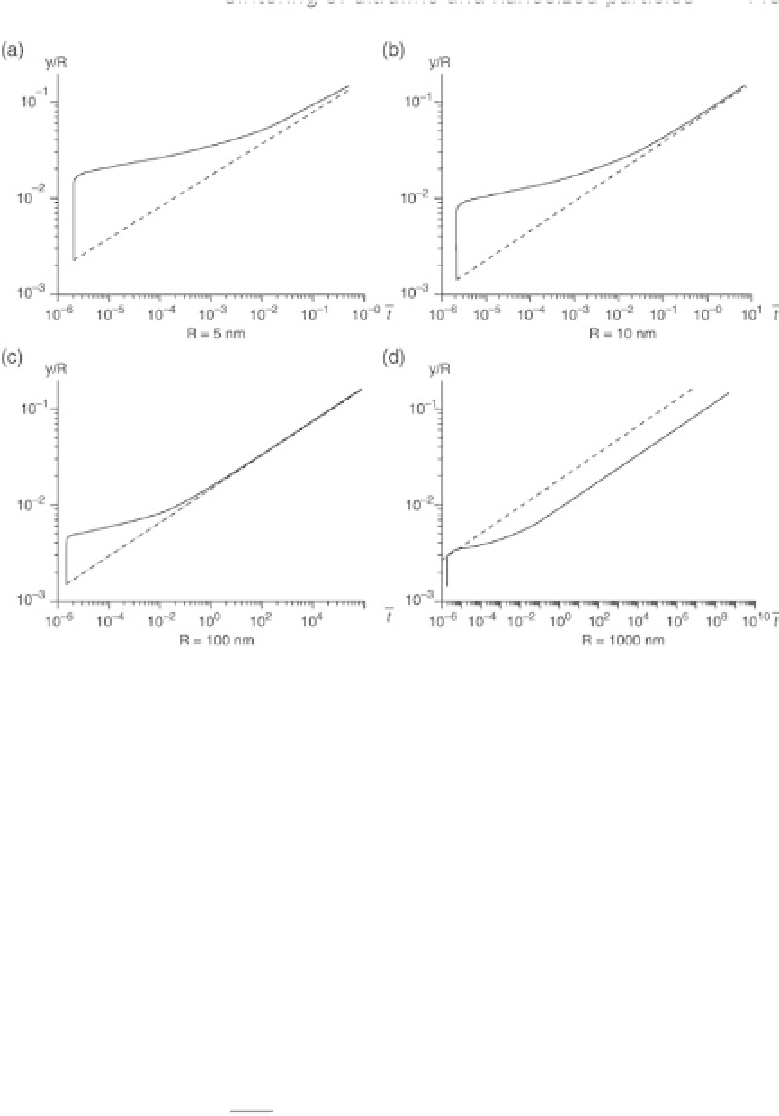
(a)-(d) Comparison between the linear solution (- - - -) and the
nonlinear solutions (—-) for the shrinkage between two spherical
particles as functions of time.
13.3.2 Kinetic theories, modeling, and simulations of
sintering of nano particles
Given the unique physics that presents when sintering nano particles, Pan
recognized that the rapid kinetic rate of sintering is a direct result of the
large driving force for sintering of nanosized particles, and revised the two-
sphere sintering model by using non-linear diffusion law.
43
Because the
diffusion is the result of jumping atoms, the flux of diffusion as a function of
the frequency of jumping (f ), volume atomic concentration (C
solid
) and the
atomic spacing (a) can be given by
2D
a
aF
2kT
¼
½
:
J
O
sinh
13
9
where D is the diffusion coefficient,
is the atomic volume, a is the atomic
spacing, F is the driving force for diffusion, and k and T are the Boltzmann
constant and absolute temperature respectively. Pan pointed out that this
equation reduces to linear diffusion law, when aF
W
kT, then sinh(aF/2kT)
≤
≈