Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
12.5
DTA curve (non-oxidizing atmosphere) of a Cu
2
(OH)
2
CO
3
-Al
mixture after the first step in mechanical treatment. The product
contains an undecomposed part of Cu
2
(OH)
2
CO
3
and unreacted Al.
This also represents a simulation of the reactions in the system that
may occur under mechanical action (SDT 2960 TA Instrument)
(Wieczorek-Ciurowa
et al.
, 2005).
inside the powder are not uniform but are concentrated at a few points. This
results in the formation of 'hot spots', where the reaction can start even if
the average temperature of the powder is not sufficient to initiate a reaction
front. Intimate contact between the reactant phases is an essential
requirement for self-propagating synthesis. This condition is easy to achieve
when mechanical activation is conducted in a system of ductile-brittle
substances.
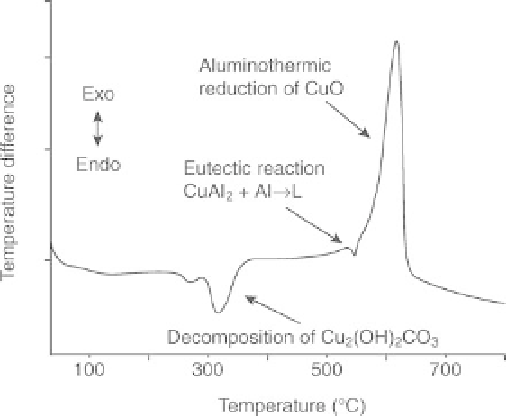
The temperature of initiation of a metallothermic reaction can be
recognized by differential thermal analysis (DTA) (strong exoeffects). This
is illustrated by the DTA curve (Fig. 12.5) for the product of the CuO-Al
powder after the first step of mechanochemical synthesis. The CuO formed
by the mechanical decomposition of Cu
2
(OH)
2
CO
3
reacts with Al, forming
copper in a combustible manner at about 600
C. This procedure can be
considered a simulation of a mechanochemical reaction (Wieczorek-
Ciurowa and Gamrat, 2007a).
An example of self-propagation reactions are processes occurring during
milling aluminium and magnetite powders in argon, given by Botta et al.
(2000) as follows:
8
3Fe
3
O
4
þ
8Al
!
9Fe
þ
4Al
2
O
3
½
12
:
1
There are two different effects, which are due to the time period of
mechanical activation. After 30 min milling, a decrease in the starting