Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
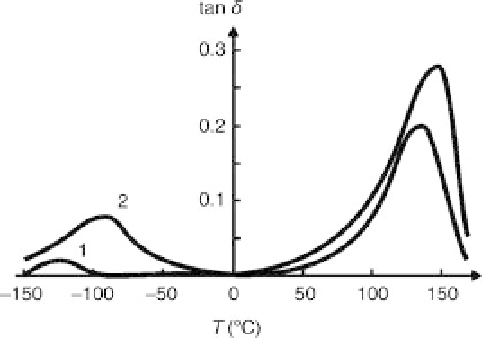
9.12 Temperature dependence of tanδ for pure SHMPE (curve 1) and
SHMPE-ceramic nanocomposite (curve 2); ceramics content (wt%)
= 15% [25].
of small particles of the filler because the formation of such aggregates can
only take place at higher degrees of filling [39]. It seems that the observed
increase in mechanical loss is a result of adsorption of the binder on the
surface of the filler and intercalation of fragments of the macromolecules
into the interlayer space of the ceramic grains. Such an interaction can
change the structure of the polymeric matrix near the boundary of the
particles and, as a consequence, yield an increase in mechanical losses.
It is known [40] that, in some cases, the filler shifts the maximum
mechanical losses and T
g
towards higher temperatures. It is assumed that
the magnitude of the shift is proportional to the surface area of the filler,
which explains the polymer-filler interaction. The non-additive contribution
of the added ceramics on the T
g
shift (Table 9.7) points not only to
adsorption interactions, but also to the intercalation of the fragments of
SHMPE macromolecules into the interlayer space of the ceramic grains, as
indicated earlier.
It is obvious that such an interaction limits the mobility of the
macromolecules, thus changing the packing density of the polymeric chains.
As a result, a morphology change around the phase boundary may occur.
To prove these considerations, the temperatures and enthalpies of melting
for a range of SHMPE-Y
1
Ba
2
Cu
3
O
6.97
nanocomposites were measured
directly, using differential scanning calorimetry (Table 9.8). With an
increase in filler content, the enthalpy of melting recalculated for the
polymer fraction (excluding the filler) increases, as shown in Table 9.8.
Again, there is some discrepancy with the curves shown in Fig. 9.11 and
9.12. In the figures, the melting peak shifts to higher temperatures with
increasing filler content. This increase in enthalpy is linked with either the
overall degree of crystallization or with a change in morphology of the