Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8.10
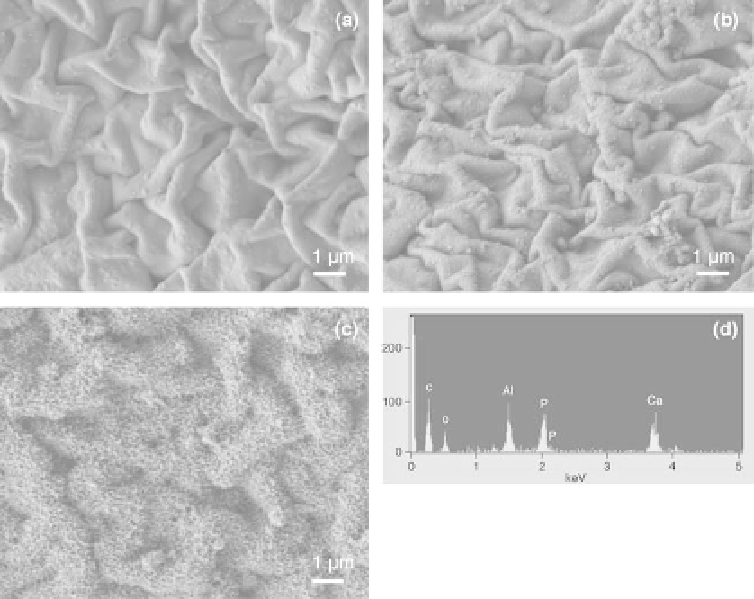
FESEM images of the polymer/alumina composite before (a) and
after incubation in SBF at 37
C for one week (b) and two weeks (c), (d)
EDS spectrum of the polymer/alumina composite after incubation in
SBF for two weeks (Liang
8
et al
., 2009). Reproduced by permission of
American Chemical Society.
ceramic ALD films provides a new class of polymer/ceramic composite
materials with potentially greater material strength and enhanced bioactiv-
ity for tissue regeneration. Future work should focus on the deposition of
ceramic films on more appropriate tissue engineering porous scaffolds that
are being used in bone tissue engineering, such as poly (lactic acid), poly
(lactide-co-glycolide) and poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (Liang et al.,
2009).
8.6
Conclusions and future trends
This chapter has reviewed the novel particle ALD process. It has been
shown that a fluidized bed reactor is a robust unit operation for the batch
functionalization of fine and ultra-fine particles using the ALD technique. In
situ mass spectrometry is a useful tool that allows for optimization of the
process variables at any scale. 100% precursor utilization was shown to be
attainable, and the surface conversion at the point of unreacted precursor
breakthrough is a function of the reactivity of the precursor. Many materials