Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8.4
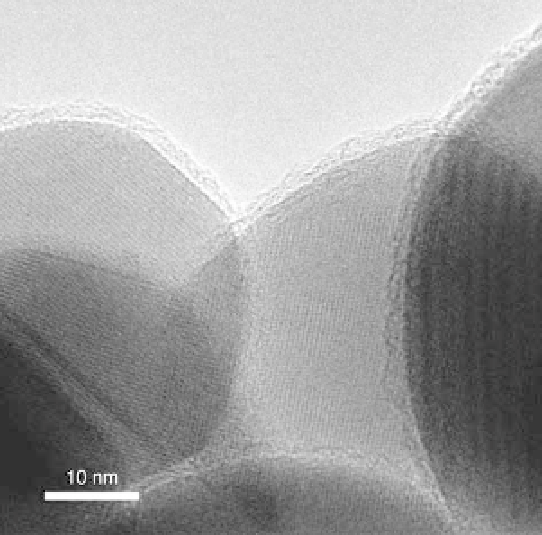
HRTEM image of 2.5 nm BN films deposited on ZrO
2
nanoparticles
(Ferguson
et al
., 2002). Reproduced by permission of Elsevier.
excess precursor waste. The process is also commercially significant since it
can operate in a simple process for practical large-scale applications.
8.2.3 Characterization of ALD thin films
Different analytical techniques are needed to verify the composition and the
uniformity of ALD films deposited on particle substrates. X-ray photoelec-
tron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), and induc-
tively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) can analyze
the composition of the ALD films. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) can
study the crystallinity of ALD films and measure the crystallite size
propagation of some ALD films with the number of cycles. Transmission
electron microscopy (TEM) is a useful technique to observe film/particle
interfaces. Normally, the particles are put directly onto Cu grids with a
holey carbon overlay film. ALD films thinner than
5 nm may be difficult to
observe using standard TEM technique alone. High-resolution transmission
electron microscopy (HRTEM) is needed for these thin films. One example
of an ultra-thin BN ALD film on ZrO
2
nanoparticles observed by HRTEM
is shown in Fig. 8.4 (Ferguson et al., 2002). The deposited films on micron-
sized particles can be better observed by cross-sectional HRTEM. Cross-
sectional TEM samples can be prepared by cutting thin slices of a cured
~