Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8.2
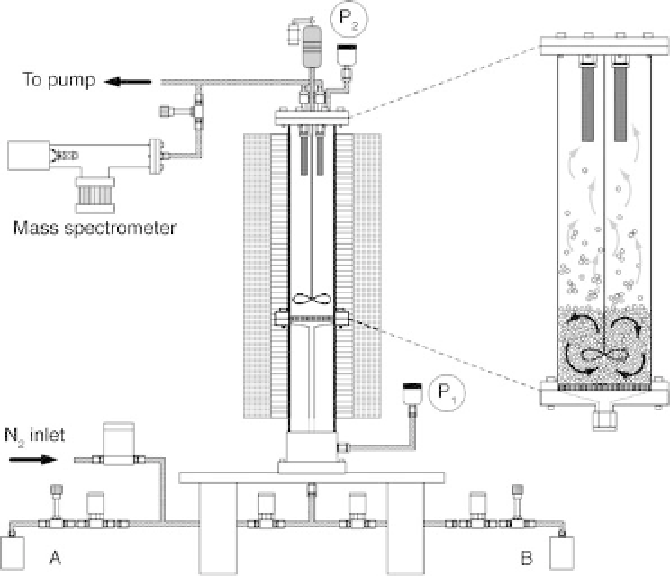
Schematic illustration of ALD fluidized bed reactor (King
et al
.,
2007). Reproduced by permission of Elsevier.
metal walls was positioned inside a vacuum chamber. The porous cylindrical
drum was rotated by a magnetically coupled rotary feedthrough.
The FBR has many advantages, including good mixing, large gas-solid
contact area, high efficiency of mass and heat transfer, and large-batch
processing capability. With appropriate expansion of a bed of particles,
granular materials are transformed into a fluid-like state through contact
with a gas or a liquid. The rigorous mixing during fluidization provides
excellent fluid-solid contacting. In an FBR system, gas precursors can be
introduced into the bed for reaction with the surface of the particles, while
the particles are circulating in a liquid-like state. Ultra-thin films can be
coated on primary nanoparticles without significant aggregation during the
ALD coating process. This phenomenon can be explained by a behavior
called dynamic aggregation (Hakim et al., 2005c), which is observed during
the fluidization of nanoparticles. The native cohesive properties of the
nanoparticles will form agglomerates that are several times larger than the
primary particles. Dynamic agglomerates partially break apart and reform
due to constant solids recirculation and gas flow through the bed of
particles. External forces, such as mechanical vibration, can improve
fluidization quality by helping to partially overcome interparticle forces.
This serves to reduce the average size and increase the disengagement rate of