Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
7.10
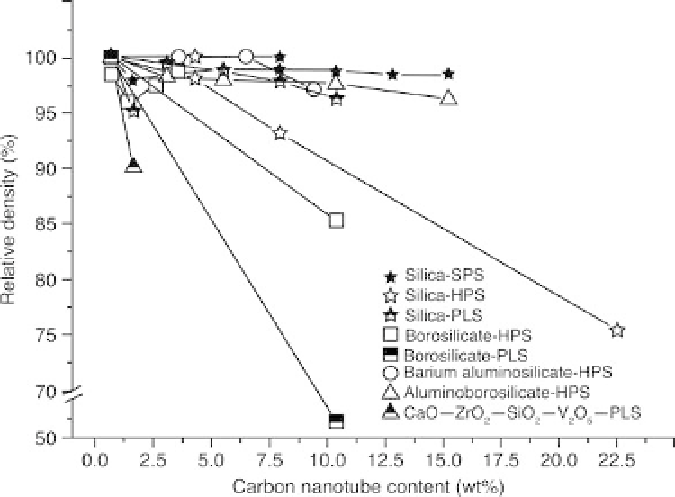
Percentage relative densities of glass and glass-ceramic matrix
composites containing CNTs available in the literature.
borosilicate composites; relative densities of only 51% were obtained
(Boccaccini et al., 2005). A change in the composite powder processing
technique from direct powder mixing to colloidal mixing provided good
density of silica glass composites, i.e. 95% of relative density for composites
with (only) 1wt% CNTs (Arvanitelis et al., 2008). Recently, the use of PLS
was revived and high CNT loadings (10wt%) were incorporated in silica
glass to achieve densities greater than 96% (Subhani et al., 2011);
comparatively lower CNTs contents (2.5-7.5wt%) showed even higher
densities of 98-99%. Glass-ceramic matrix composites have been also
densified by PLS, for example, CNT-CaO-ZrO
2
-SiO
2
and CaO-ZrO
2
-
SiO
2
-V
2
O
5
matrix composites containing 1wt% CNTs, but these showed
only 90% relative density (Giovanardi et al., 2010).
7.6.2 Mechanical properties
Four mechanical properties of CNT-glass/glass-ceramic matrix composites
have been investigated in most studies - hardness, elastic modulus, fracture
strength and fracture toughness. The incorporation of CNTs in glasses/
glass-ceramic matrices has led to different effects on these properties, as is
now explained.