Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
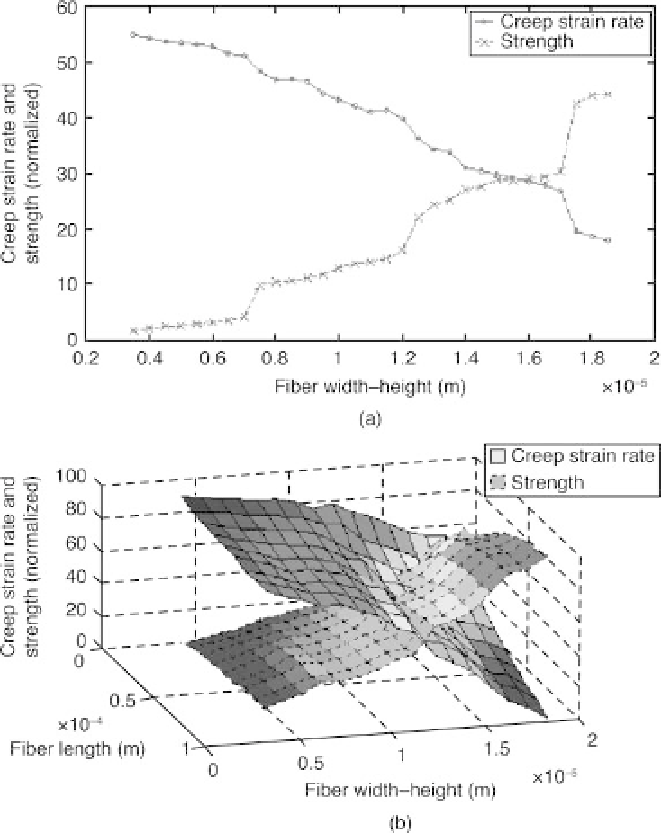
5.4 (a) Strength and creep strain rate at 1500
C as a function of the
design variable width-height (d) for the 2D low-fidelity model. (b)
Strength and creep strain rate at 1500
8
C as a function of the design
variables width-height (d) and length of fibres (l) for the 3D high-fidelity
model.
8
Figure 5.4 illustrates normalized (0-100) function values for the strength
and creep strain rate as a function of design variables for the high-fidelity
model (3D) and low-fidelity model (2D). Figure 5.4(a) shows an increase in
the CFCC strength and a corresponding decrease in the creep strain rate as
the design variable d increases. Similarly, for the high-fidelity model,
Fig. 5.4(b) shows an increase in the CFCC strength and a corresponding
decrease in the creep strain rate as the design variables d and l increase.