Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4.2
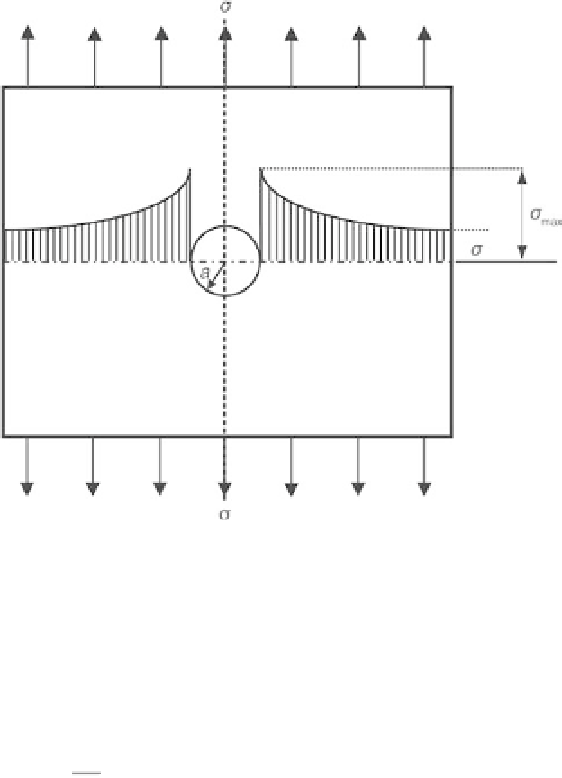
Stress distribution in a plate containing a circular hole.
relations for surface energy
γ
and rupture strength
σ
f
:
Ea
0
p
g ¼
½
4
:
1
2
1
=
2
E
g
a
0
E
p
s
f
¼
%
½
:
4
2
where E is the modulus of elasticity and a
0
is the interatomic distance. The
value of
is difficult to determine, and this model gives most materials
unrealistically high values of rupture strength. The reason for this is the
presence of structural defects, which act as stress concentrators (Fig. 4.2).
The stresses at their tips can easily exceed the theoretical cohesive strength
of the material, so leading to crack propagation and failure.
γ
4.2.2 Fracture toughness
Linear elastic fracture mechanics is used for the basic description of crack
propagation through a solid brittle material. Its basic assumptions may be
summarised as follows.
1. The material behaves like a linear elastic continuum: no non-elastic
deformations are considered. This is usually a good approximation of a
ceramic material.