Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
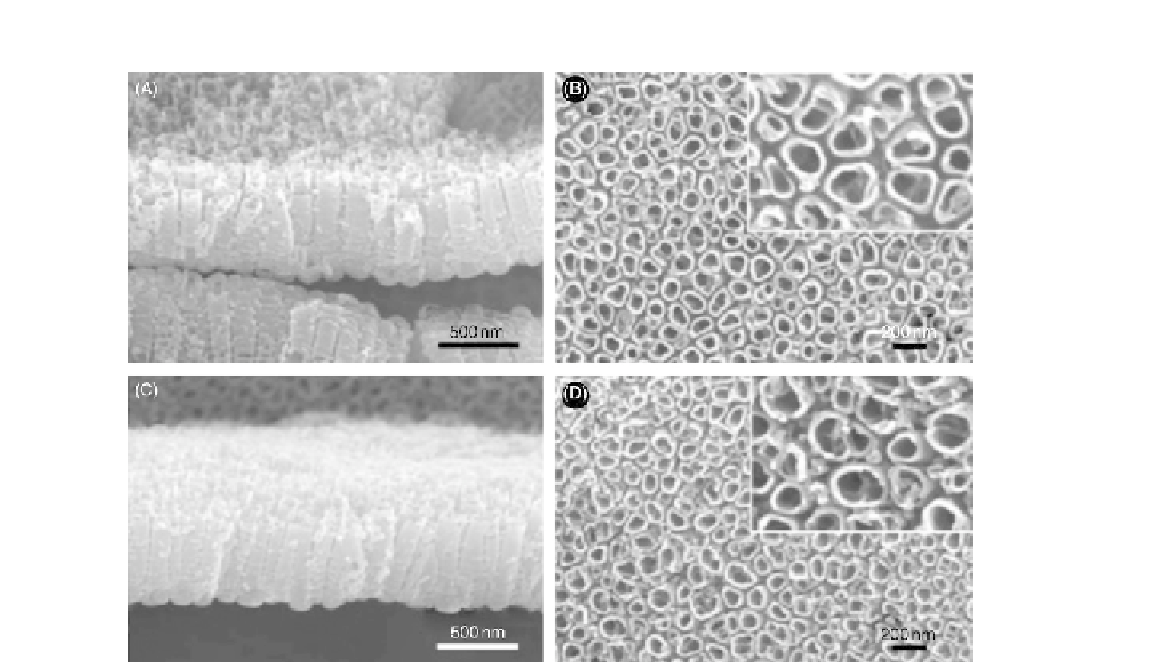
FIGURE 18.1
FESEM of TiO
2
nanotubes (A) machined transverse view, (B) machined plan view, (C) restorable blast
media transverse view, and (D) restorable blast media side view
[6]
.
surface height. There are two modes of operation for the STM, the constant height and the constant
current mode. In constant current mode, as the tip is scanned laterally over the surface the tip height
is moved in order to keep the current constant. The movement of the tip height is used to profile the
surface. In constant height mode, the height and tip voltage are held constant. The change in current
required to keep the voltage constant is related to local charge density to provide a record of the sur-
face profile. Constant height mode is faster than constant current as piezoelectric movements in con-
stant current require more time than the electronic control to keep voltage constant in constant height
mode. This can provide a significant advantage as typical STM measurements for area profile record-
ing can be very time consuming. Appropriate sample handling and preparation procedures need to be
developed for each material type to be examined
[8-11]
. Organic molecules can be imaged with STM
when placed on a conducting substrate. It is important to minimize resolution loss due to unwanted
mixing between molecular and substrate electronic levels. Better resolution can typically be achieved
at ultrahigh vacuum (UHV); however, samples can provide difficulties with ultralow vapor pressures
or decomposition or which denature at elevated preparation temperatures. The benefits of using pas-
sivated substrates have been demonstrated for the capturing of organic molecules to allow examina-
tion with UHV STM.