Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
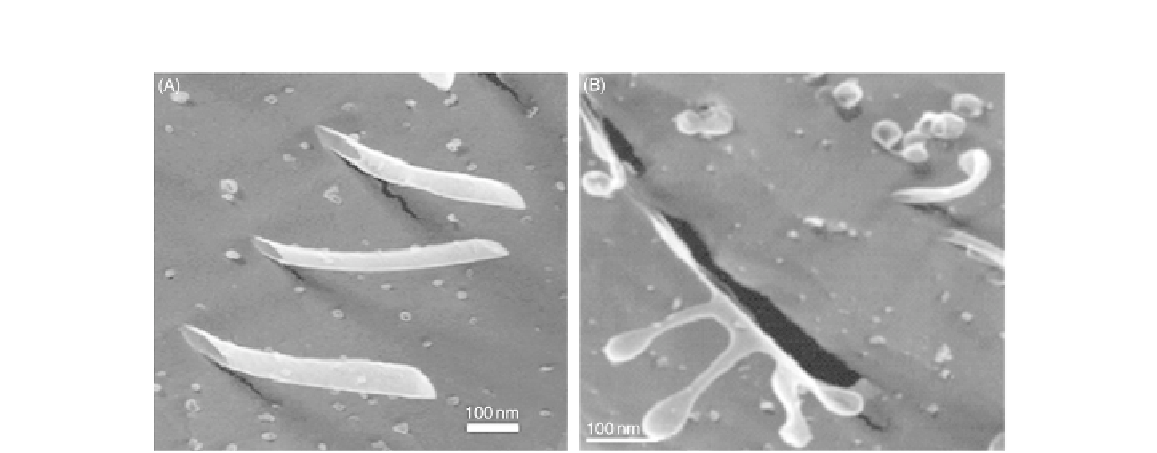
FIGURE 13.9
Quick-freeze/deep-etch transmission electron micrographs of V6D peptide complex. (A) Nanotubes with a
diameter of 30-50 nm; (B) Nanovesicles and nanotubes.
Image credits:
[12,17]
.
amphiphilic peptide molecules have a hydrophilic (polar) and a hydrophobic (nonpolar) component. In
aqueous solution, they self-assemble into distinct structures whose shape is largely determined by the
size and shape of the hydrophilic polar head. These molecules have one or two amino acids in the polar
region and four or more consecutive hydrophobic amino acids in their nonpolar end. One such example
described is the V6D amino acid complex
[17]
. The V6D amino acid sequence (VVVVVVD) has six
valine (V) residues that are hydrophobic and an aspartic acid (D) residue that is negatively charged.
Valine (α-aminoisovaleric acid) is an essential amino acid and aspartic acid a nonessential amino acid.
In aqueous solution the V6D peptide complex self-assembled to form various nanostructures like nano-
tubes and nanovesicles (
Figure 13.8
). The samples of the aqueous solution were frozen in liquid propane
(
180°C) and surface-coated with a thin layer of platinum and carbon to preserve the structures formed
and when investigated using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Zhang et al.
[12,17]
observed
nanotubes and nanovesicles (
Figure 13.9
). The nanotubes measured about 30-50 nm. The researchers
concluded that the self-assembled structure can be modified by changing the sequence of the amino
acids in the peptide chain and the environmental factors. These peptide nanotubes can be incorporated
into self-assembled membranes for application in nanobiosensor devices
[17]
.
The researchers also suggest that these surfactant peptides can be engineered for improved func-
tionality by using a technique called biotinylation
[12]
. Biotinylation is a process of incorporation of
biotin groups into molecules to visualize specific substrates by incubating them with biotin-labeled
probes and avidin or streptavidin
[28]
. It is a rapid method of detecting nucleic acids for use in
Western blot technique
[29]
. When these surfactant peptide nanostructures are made to undergo the
process of biotinylation, they can be bound to streptavidin-coated inorganic metal surface. Histidine-
tagged peptides and proteins can be bound to nickel surfaces. Thus by utilizing the standard tech-
niques in peptide chemistry, these nanostructures can be bound to metallic surfaces.