Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
13.6
PEPTIDE NANOFIBERS, NANOTUBES, AND NANOWIRES
Stupp et al.
[13]
utilized the change in pH to induce self-assembly of amphiphilic peptides to nanos-
cale fibers which formed nanostructured fibrous scaffold reminiscent of extracellular matrix (ECM).
In a later study, Stupp et al.
[14]
fabricated nanofibers by exploiting the electrostatic attraction
between two bioactive peptide-amphiphile molecules. Artificial proteins that self-assemble to form
hydrogels in response to pH and environmental changes have been reported by Tirrell et al.
[15]
. The
self-assembling proteins were made up of ionic self-complementary peptide group that had an alter-
nating polar and nonpolar fashion of arrangement of peptide molecules. These peptides formed a sta-
ble β-strand and β-sheet structures which self-assembled to form nanofibers. These nanofibers formed
interwoven matrices that self-assembled to form a scaffold hydrogel with high water content (
Figure
13.3
). Hydrogel has water as its dispersion medium and responds to changes in pH and other environ-
mental factors. These protein hydrogels can be used for advanced wound closure and tissue repair in
regenerative medicine
[16,17]
and tissue engineering
[18,19]
. Biodegradable self-assembled protein
and peptide nanofibers can also act as target-specific drug delivery systems delivering drug molecules
[20]
. Immunohistochemical studies of self-assembling peptides injected
in vivo
did not show obvious
inflammation or immune response, thus demonstrating that self-assembled peptides can act as effec-
tive drug delivery systems with better biocompatibility
[21,22,23]
.
The self-assembling amphiphilic peptide molecules have also been utilized as scaffolds to fabri-
cate nanowires. A nanowire is a solid metallic cylinder-like structure with a diameter ranging from
10 nm to a several 100 nm
[12]
. The amphiphilic peptide nanotubes can be used as templates for met-
allization
[13]
. One such example of the peptide sequence used was the histidine-rich peptide nano-
tubes (
Figure 13.4
). This structure was metallized with gold nanocrystals and the organic peptide
scaffold was removed to make a conducting gold nanowire
[14-16]
. Specific peptide sequences rec-
ognize specific metal ions and bind to them. Thus by varying the peptide sequence, much efficient
metal coatings can be coated on peptide nanotubes. The examples of other efficient metals that can be
coated on peptide nanotubes are silver, platinum, copper, and nickel. Zhang et al.
[12]
have designed
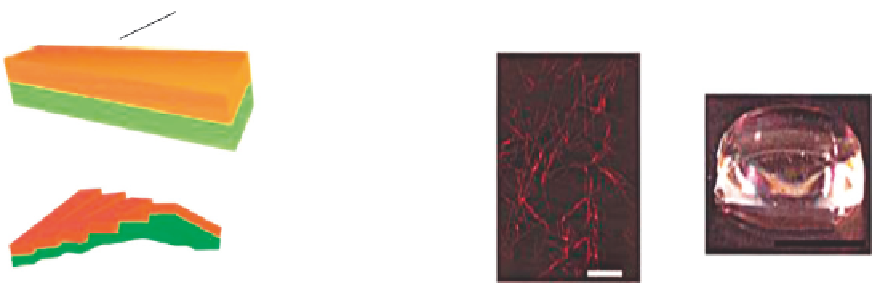
Hydrophilic
Single molecule
(
β
-strand conformation)
Hydrophobic
1 cm
β
-sheet tape
500 nm
FIGURE 13.3
Amphiphilic peptides in
β
-strand and
β
-sheet conformation self-assemble into interwoven matrices that further
form a scaffold hydrogel.
Image credits:
[12]
.