Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
SYNTHETIC EMULSIFIERS
M
ONO
-
AND
D
IGLYCERIDESOF
F
ATTY
A
CIDS
The most commonly used emulsifiers in the food industry are mono- (MG) and
diglycerides (DG). These are prepared commercially by direct esterification of edible
fats or fatty acids (from vegetable or animal origin) with glycerol at elevated tem-
peratures, or by interesterification of an oil with glycerol.
4,83
During transesterifica-
tion, triglycerides are heated with glycerol and a catalyst, usually sodium hydroxide,
under vacuum at 200°C. As the fatty acids are hydrolyzed from the triglycerides,
some re-esterify at other free hydroxyl positions to form mono- and diglycerides.
84
The yield of MG depends on the proportion of triglyceride to glycerol used. Such
methods were demonstrated by reacting the oils of coconut, peanut, sesame, linseed,
and sardine and direct esterification of fatty acids with glycerol.
85
Feuge and Bailey
86
demonstrated that the proportions of glycerol, mono-, di-, and triglycerides can be
calculated statistically based on two assumptions: The reaction between admixtures
from either method contains traces of free glycerol and free fatty acids, which can
be removed by distillation. Commercial MG usually contain about 40 to 50%
monester, 40% diester, and 10% triglycerides.
87
Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids exist in several structural modifications
(
Figure 7.4
).
In monoglycerides, if the fatty acid is attached to the middle carbon
atom, the molecule is symmetrical and the monoglyceride can be termed a beta-
monoglyceride. When the reaction is carried out at 20°C the relative proportions of
O
CH
2
-O-C
CH
3
CH-OH
1 - Monoglyceride
CH
2
-OH
CH
2
-OH
-H
2
O
C
CH
2
-OH
O
+
OH
+
CH
3
C
CH-OH
CH
2
-OH
CH-O-C
CH
3
-H
2
O
2 - Monoglyceride
CH
2
-OH
Fatty acid
Glycerol
O
CH
2
-O-C
CH
3
O
CH-O-C
CH
3
1, 2 - Diglyceride
O
CH
2
-OH
CH
2
-O-C
CH
3
CH
2
-OH
CH-OH
O
O
CH
2
-O-C
CH
3
CH-O-C
CH
3
CH
3
O
CH-OH
1, 3 - Diglyceride
CH
2
-O-C
O
CH
2
-OH
CH
2
-O-C
CH
3
Triglyceride
Glycerol
O
CH
2
-O-C
CH
3
CH
3
O
Triglyceride
CH-O-C
O
CH
3
CH
2
-O-C
CH
2
-OH
O
+
CH-OH
CH
3
C
OH
Glycerol + Fatty acid
CH
2
-OH
FIGURE 7.4
Preparation of monoglycerides of fatty acids by: (I) Transesterification of fats
with glycerol, and (II) direct esterification from fatty acids, at elevated temperatures and in
the presence of alkaline catalyst.
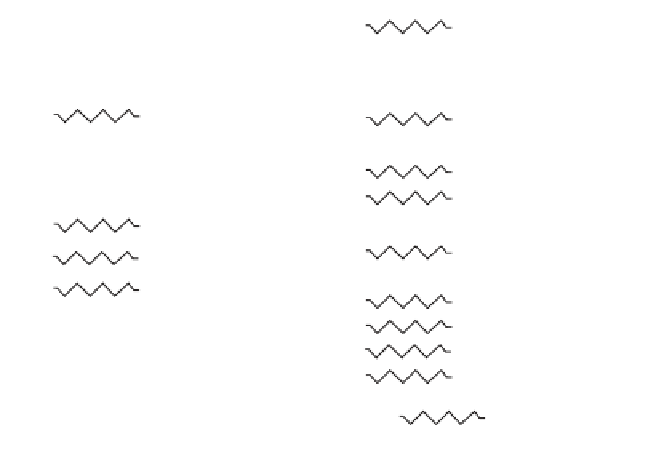




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search