Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
mean that it is a promoter! Plasmids generally expose “naked” DNA, de-
void of histones and nucleosomal structures common to DNA present in
chromosomes. Therefore, it is important to determine the “accessibility”
of the DNA in the cell using other methods (see below).
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)
An EMSA or
band shift
is used to detect the interactions between
DNA binding proteins (including transcription factors) and a DNA se-
quence recognized by those proteins. This method was developed in
1981 (27) as a rapid and semiquantitative method for identifying protein
interactions with specific DNA sequences. EMSA works well with crude
nuclear extracts from cells or purified proteins produced by recombi-
nant DNA methods. Extracts or purified proteins are incubated with a
radiolabeled dsDNA probe containing the putative recognition site.
The dsDNA can come from cloned DNA from a putative promoter or en-
hancer sequence, or oligonucleotides containing known protein binding
motifs (or mutations of these). The DNA-protein complexes are then
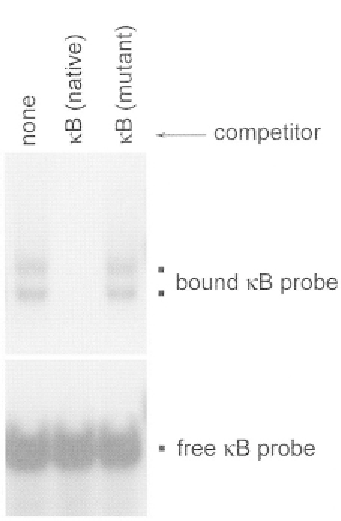
separated from the free probe by nondenaturing PAGE, and the gel is
exposed to film. While the free probe will migrate rapidly, the bound
probe will be “retarded” in the gel and migrate more slowly. Figure 6
Figure 6. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
Search WWH ::

Custom Search