Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
“packaged” into an infectious particle. Two types of bacteriophages are
commonly employed for recombinant DNA technology, bacteriophage
lambda and its derivatives, and M13. M13 produces, in addition to
dsDNA, a single stranded DNA which facilitates DNA sequencing. The
introduction of DNA into a bacterium by infection with a bacteriophage
is called transduction. The bacteriophages replicate within the bacteria,
eventually leading to their destruction (also called lysis), releasing the
phage particles, which can then infect adjacent bacteria. When bacte-
riophages are used to infect a lawn of bacteria grown on an agar plate,
they produce viral plaques, which are clear circular regions on the bac-
terial lawn that result from the lysis of a number of adjacent bacterial by
the viral progeny of a single initial infectious virus.
Bacteriophage
vectors
Bacteriophage vectors are useful for the production of
cDNA
li-
braries and genomic libraries (see below). Bacteriophages are used for
the construction of libraries because DNA can be cloned with high effi-
ciency. In addition, these viruses can accommodate large DNA inserts
which are much larger than can be cloned into most plasmid vectors.
These inserts are packaged into the phage heads. Examples of com-
monly used bacteriophage vectors include and and the
EMBL vectors. and are used for the high efficiency cloning
of cDNA libraries (20). is used strictly for the cloning of cDNA
libraries, which are screened by hybridization of viral plaques. dif-
fers from in that the cloned DNA is expressed as a stable bacterial
fusion protein with are screened using antibodies
specific for a protein of interest. This was at one time the most efficient
method of isolating cDNA encoding a particular protein, but other vectors
are now available. The cDNA can then be used to identify and charac-
terize the corresponding gene, as well as provide sequence information
on the nature of the protein itself.
vectors were designed for the cloning and manipulation of
genomic DNA (21).
M13 phage vectors
M13 is a family of vectors derived from the bacteriophage M13. These
contain a circular, single stranded DNA genome. Once E. coli are in-
fected by M13, the phage produces a double-stranded DNA replica-
tive form (RF), which multiplies while continuously producing single
stranded phage that are released into the growth media. Because they
produce large amounts of single stranded phage which are also easy
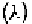






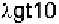
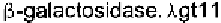
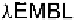
Search WWH ::

Custom Search